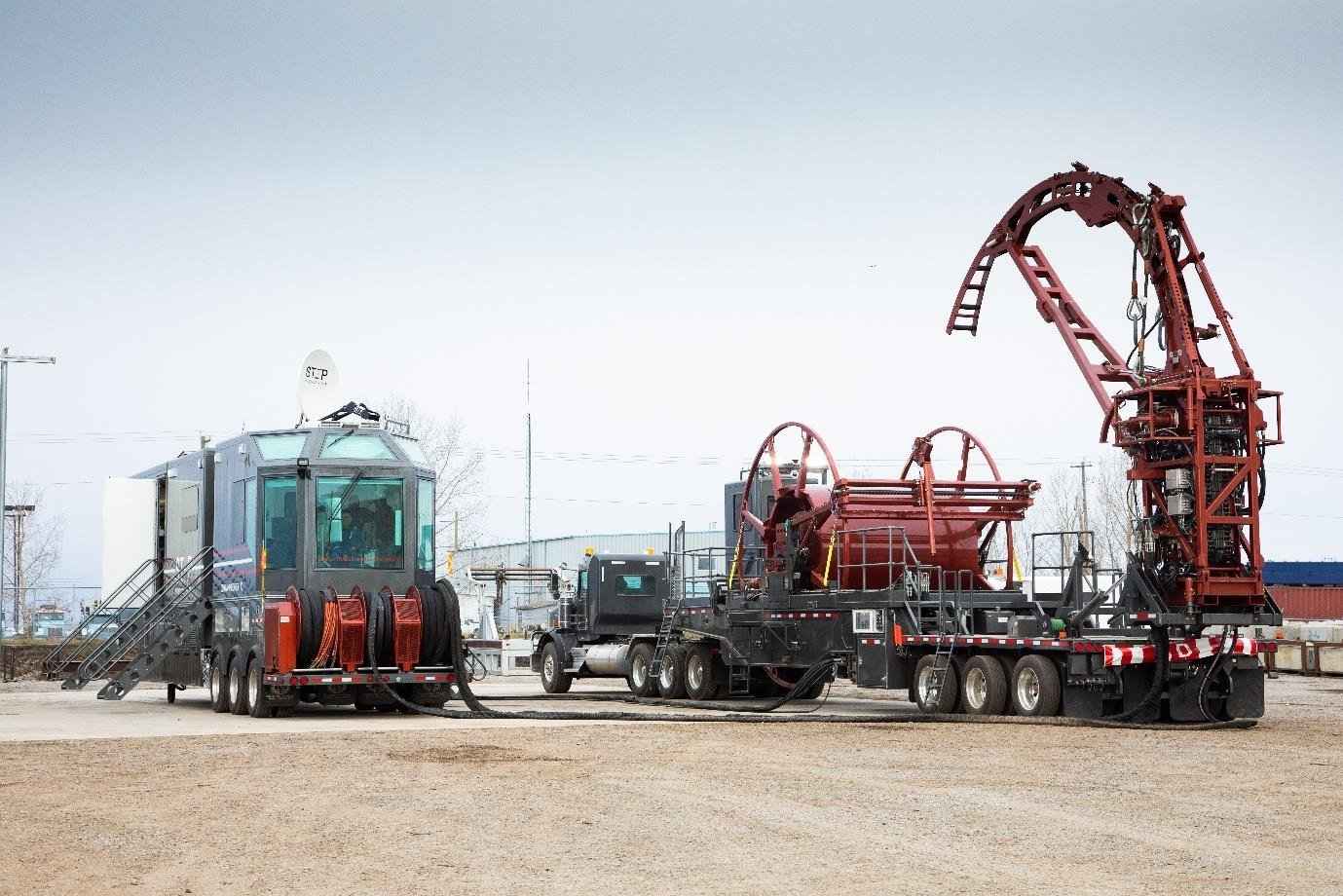
Coiled tubing (CT) has become one of the most transformative technologies in modern well intervention operations. In today’s oil and gas industry—where efficiency, precision, and uptime define profitability—coiled tubing offers a powerful way to perform complex downhole tasks without the need for costly workovers.
As oil and gas wells age, production naturally declines due to issues such as scale buildup, paraffin deposition, or formation damage. Conventional intervention methods often demand heavy equipment, long downtime, and high operational risks. Coiled tubing changes this narrative—providing a safer, faster, and more flexible solution that restores well productivity while minimizing disruption.
What Is Coiled Tubing?
In the petroleum industry, coiled tubing is a continuous metal pipe with no joints ranging from 1 to 3.25 inches (25 to 83 mm) in diameter conveniently supplied spooled on a large reel. This coiled tubing serves multiple purposes, including interventions in oil and gas wells and production tubing in depleted gas wells.
What Is Coiled Tubing Operation?
In the oil and gas sector, coiled tubing operation is a technique used for well intervention without using traditional drill pipes. It employs a continuous coil of tubing, typically made of steel or composite material, wound onto a large spool and then inserted into the wellbore. This method allows for various tasks to be performed in the wellbore efficiently. Coil tubing is sometimes needed when the well completion and workover are performed.

Operators use coiled tubing for various tasks, including well cleanouts, acid stimulation, fracturing, cementing, logging, plug setting or retrieval, and stuck pipe prevention. They deploy the coiled tubing into the wellbore through a specialized injector head that controls its speed and tension. After reaching the desired depth, they run various tools and equipment through the tubing to perform the required tasks.
What Are The Application of Coiled Tubing?
Since coiled tubing is a versatile tool in the oil and gas industry, it simplifies and supports various drilling applications.. Circulating, pumping, coiled tubing drilling, production, logging and perforating commonly apply coiled tubing.
1. Circulation
Coiled tubing is a beneficial tool for circulation in well interventions due to its continuous length ability to navigate complex wellbores. In some cases, a hydrostatic head’s weight impedes the flow of formation fluids in a well. To restore the flow, operators insert coiled tubing into the wellbore, allowing production to resume.
2. Pumping
Another common application of coiled tubing is for pumping operations in oil and gas wells to deliver various fluids and treatments. It is employed in applications such as hydraulic fracturing, well stimulation, cementing, acidizing, and nitrogen purging.
To initiate pumping, the coiled tubing is connected to a surface pumping unit or a dedicated pumping system. Fluids are then pumped down the coiled tubing string, which is inserted into the well. The continuous length of coiled tubing enables uninterrupted pumping, ensuring a consistent and controlled flow rate.
3. Coiled Tubing Drilling
As the name conveys, coiled tubing can be employed for Coiled Tubing Drilling (CTD) operations that involve utilizing a coiled tubing string as a drill pipe to carry out drilling tasks in oil and gas wells.
In Coiled Tubing Drilling, the coiled tubing is inserted into the well and equipped with a bottom hole assembly that comprises a drill bit. The coiled tubing is then rotated and pushed into the rock formation, enabling the drill bit to cut through the rock and establish a wellbore.
4. Logging and Perforating
In logging operations, engineers use coiled tubing to lower specialized tools into the wellbore and collect subsurface data.
Operators connect logging tools and sensors to the coiled tubing string and use them to measure formation pressure, temperature, fluid composition, and rock properties. The acquired data aids in assessing reservoir characteristics and making informed decisions regarding production strategies.
5. Production
Operators use coiled tubing in production operations to perform various activities that maximize well productivity. One common application is well stimulation, where they inject fluids, chemicals, or proppants through the coiled tubing string into the well. This process enhances the performance of the reservoir, leading to an increase in hydrocarbon production.
What Are The Physical Characteristics of Coiled Tubing Equipment?
Considered as flexible yet durable, coiled tubing has several physical characteristics.
1. Self Contained
Coiled tubing earns the label “self-contained” because it includes all essential components and equipment, allowing it to operate independently without external support.
2. Mobile/Modular
Coiled tubing is mobile and modular due to its design which facilitates convenient transportation and assembly. Its modular construction allows for easy setup and dismantling, enabling it to move and deploy in different locations as required.
3. Hydraulically Powered
Coiled tubing is hydraulically powered, utilizing hydraulic pressure for efficient operation. It enables tasks such as fluid pumping, circulation, and tool manipulation, ensuring effective performance in various applications.
4. Environmentally Friendly
Coil tubing is recognized for its environmental friendliness as it contributes to minimizing ecological impacts. By reducing the requirement for extensive equipment and infrastructure, coiled tubing helps decrease emissions and disturbances to surrounding ecosystems.
What Are The Components of Coiled Tubing Equipment?
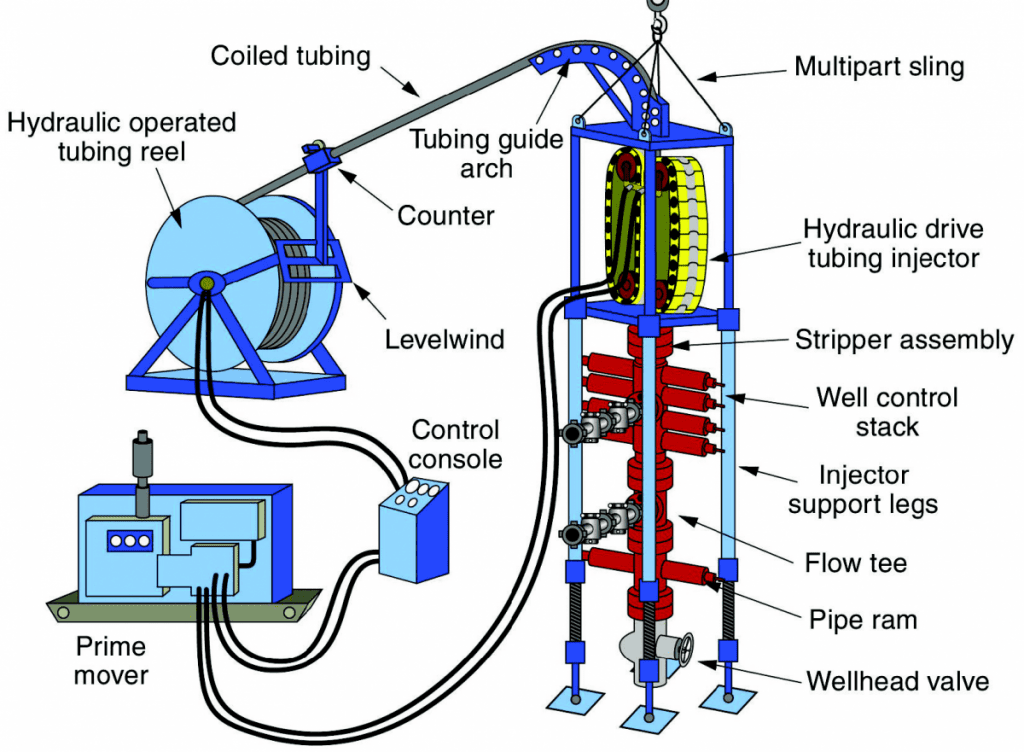
Ever since it was officially developed in late 1960, Reel tubing has become a crucial piece of equipment in the oil and gas industry for well-intervention purposes. It comes in various designs and types available in the market, but the components of a Reel tubing unit are generally similar. Here are the basic components of Reel tubing Units:
1. Injector and Tubing Guide Arch
The Reel tubing injector is a device that grasps and exerts the necessary force to deploy and retrieve the continuous Reel tubing in and out of the wellbore.
2. Service Reel with CT
The Reel tubing injector is a device that grasps and exerts the necessary force to deploy and retrieve the continuous tubing in and out of the wellbore. It is an essential component of the equipment used.
3. Power Supply or Prime Mover
Diesel engines and multistage hydraulic pumps, with pressure ratings from 3,000 to 5,000 psig, power most prime mover packages in coiled tubing units. This configuration generally defines the prime mover packages used in these units.
4. Control Console and Monitoring Equipment
The console contains the necessary controls and gauges to operate and monitor the components of the Reel tubing unit, including the red and injector heads, and the control system for regulating the drive chain, stripper rubber, and blowout preventers.
5. Downhole CT Connectors and Bottom Hole Assembly (BHA) Components
In coiled tubing (CT) services, various connections isolate pressure and transfer tension, compression, and torsional loads from tools and bottom hole assemblies to the tube.
6. Well-control Stack Equipment
The well-control stack system plays a crucial role in the pressure containment package of a Reel tubing (CT) unit, consisting of a stripper assembly and hydraulically operated rams.
How Does Coiled Tubing Work?
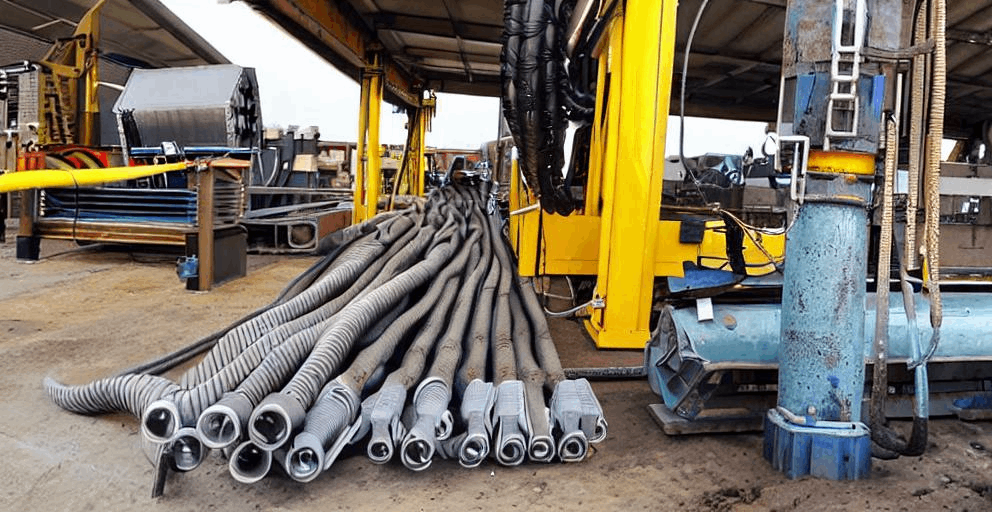

A coiled tubing unit (CTU) uses a reel of flexible steel pipe, spooled through a gooseneck into the injector head. It becomes straight before it enters the borehole. After the operation, the tubing is retrieved and spooled onto the reel while the operator controls it hydraulically.
It is important to note that a dynamic seal around the tubing string is provided by a stripper assembly beneath the injector head, which is crucial for running the CT in and out of live wells. A secondary and backup pressure-control system is provided by a blowout preventer assembly positioned between the stripper and wellhead.
The CTU control cabin manages and coordinates flexible tubing deployment and retrieval during CT surface operations.
What Are The Disadvantages of Coiled Tubing?
One disadvantage of CT is its inability to rotate. This means you can not turn the pipe, which limits its flexibility and capability in certain operations.
Another disadvantage is the risk of fatigue and wear on the tubing due to repeated bending and straightening during use. Over time, this can weaken the tubing and increase the likelihood of failure, leading to potential safety hazards and increased maintenance costs.
What Are The Advantages of Using Coiled Tubing?
Utilizing coiled tubing provides numerous benefits across different industries and applications. Here are some of the key advantages of using coiled tubing:
1. Versatility
Reel tubing is highly adaptable and can be utilized for various operations such as well intervention, stimulation, cleanouts, logging, and production enhancement. Its flexible nature allows it to navigate complex wellbore configurations efficiently.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Reel tubing operations often require smaller crews and equipment since killing well is unnecessary, leading to cost reductions. It enables faster deployment, minimizing the need for time-consuming rigging-up processes and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
3. Time Savings
Reel tubing operations are generally faster compared to traditional methods as there is no need for frequent trips in and out of the wellbore. This enables swift mobilization, increases well productivity, and reduces downtime.
4. Enhanced Well Control
The continuous length of reel tubing minimizes the risk of connection failures, ensuring better well control during operations. Real-time monitoring and control capabilities allow for immediate response to well conditions.
What Are Some FAQs Regarding Coiled Tubing?
Frequently asked questions regarding coil tubing revolve around the size and the components of the tools itself.
1. What Are The Unit Sizes of Coil Tubing?
The unit sizes of reel tubing are measured by their outside diameter (OD). These sizes vary from 0.750 inches (19.1 mm) to 5.00 inches (127 mm). Additionally, the wall thicknesses of reel tubing range from 0.087 inches (2.00 mm) to 0.337 inches (8.60 mm).
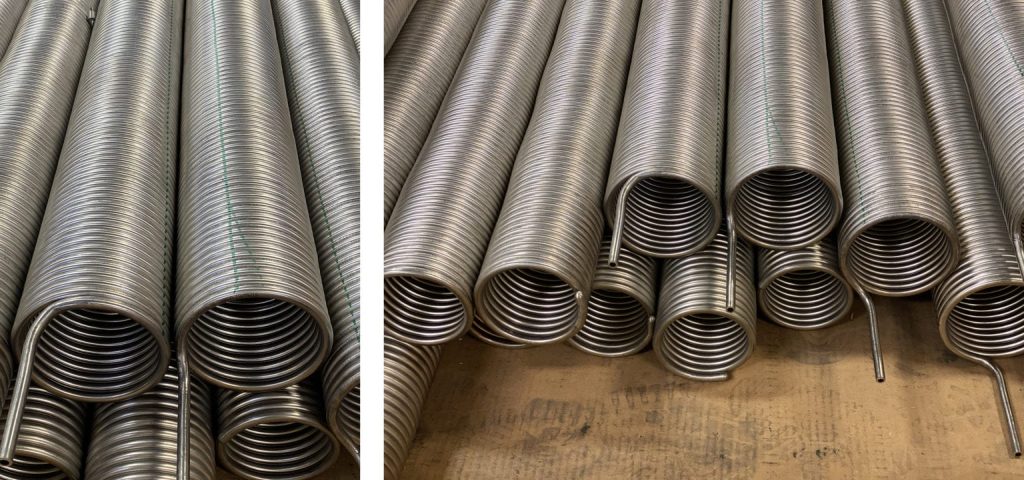

2. What Is The Length of Coiled Tubing?
Reel tubing length varies by pipe diameter (1–4.5 inches) and spool size, typically 2,000–15,000 feet (610–4,570 meters). For further information, you can refer to “The Defining Series: Introduction to reel tubing.” Reel tubing requires strict compliance with regulations—get proper training to improve your skills and expertise.
Our Coiled Tubing Operation training course provides an introductory overview of reel tubing operations in oil fields, including its concept and applications. PetroSync crafts a thorough outline covering various reel tubing technologies, focusing on surface equipment and downhole tools. It also addresses the main components, application envelope, special reel tubing applications, and contingency planning for different operational situations.
PetroSync aims to enhance your understanding, knowledge, and decision-making abilities related to wellbore treatments for well performance improvement through presentations, case studies, group discussions, exercises, and practical videos of real-world cases. Join us and gain a comprehensive understanding of reel tubing operations and their applications in oil and gas from our expert instructor!
Credit header image: stimline.com

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.