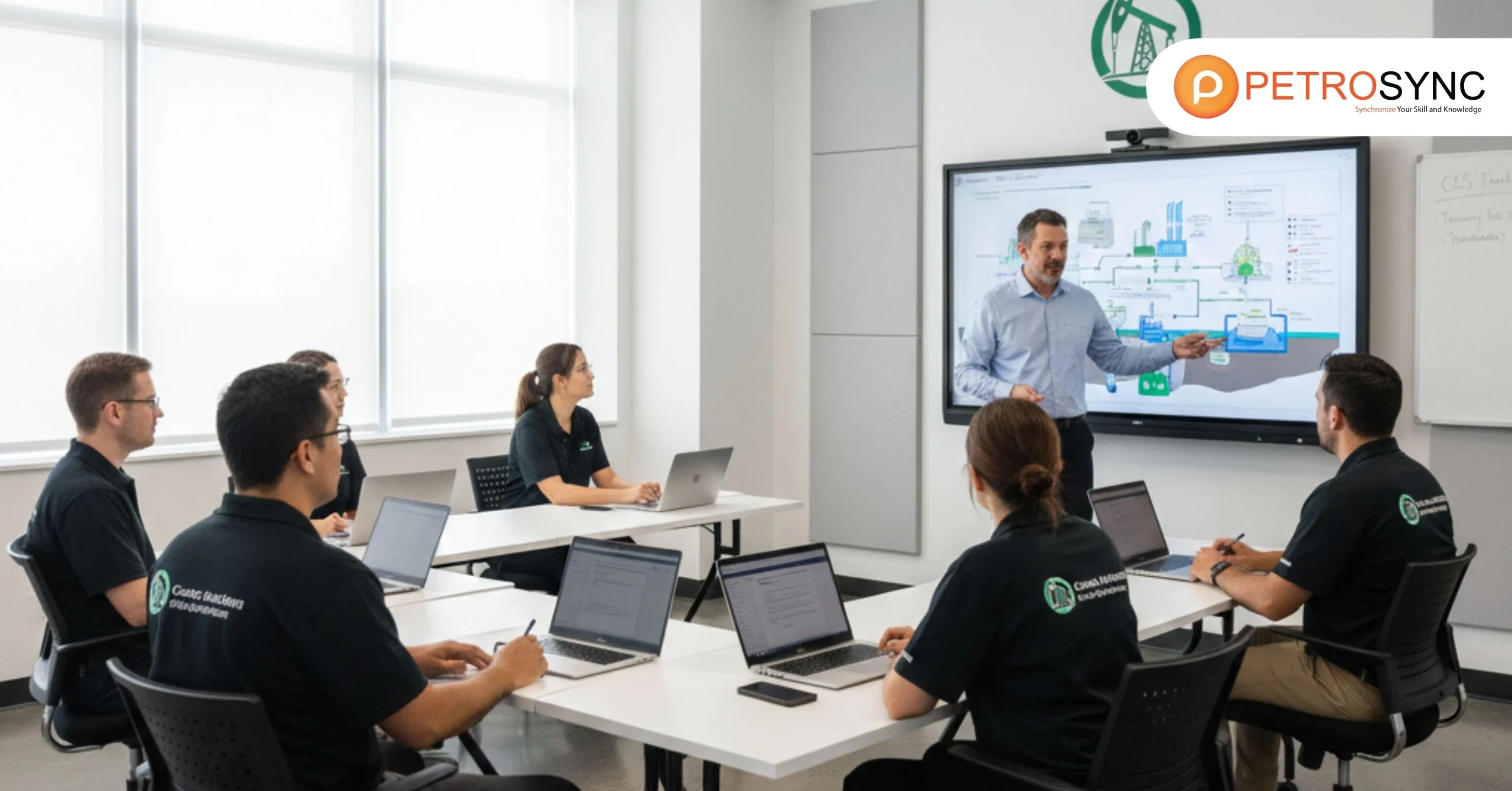
⦁ Carbon Capture & Storage is a strategic capability shaping investment choices, compliance readiness, and long-term sustainability across energy and heavy industry.
⦁ CCS enables deep emission cuts in hard-to-abate sectors without disrupting core operations, making it one of the few scalable decarbonization solutions.
⦁ CCS courses build executive confidence in evaluating capital risks, regulatory demands, and long-life project economics tied to carbon management.
⦁ Training strengthens cross-functional alignment by helping leaders translate technical, financial, and ESG priorities into coherent CCS decisions.
⦁ Structured CCS learning unlocks new value through smarter planning, stronger ESG positioning, and opportunities in transport, storage, and partnerships.
Carbon Capture & Storage courses are becoming essential learning pathways for today’s energy executives. As global industries accelerate toward low-carbon operations, the need for leaders who understand CCS technologies, economic implications, and long-term regulatory expectations continues to rise.
In many organizations, CCS is no longer viewed as a technical concept—it has evolved into a strategic capability that influences investment decisions, operational planning, and corporate sustainability commitments. In an era where companies must maintain reliability while preparing for stricter environmental expectations, CCS training provides clarity for navigating uncertainty.
The world’s major energy and industrial sectors—ranging from petrochemicals to refining and heavy manufacturing—are shifting toward decarbonization. Within this transition, CCS has emerged as one of the few scalable solutions capable of mitigating emissions from processes that cannot easily be replaced with renewables.
Before exploring why CCS courses matter for energy professionals, it is helpful to understand how CCS works and why it has become a central pillar in future energy strategies.
What is Carbon Capture & Storage?

Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) is a suite of technologies designed to capture carbon dioxide emissions from industrial or power-generation facilities and store them safely underground. The primary goal is to prevent CO₂ from entering the atmosphere, effectively reducing greenhouse gas concentrations.
Global climate and energy assessments frequently highlight CCS as a key contributor to long-term emission reduction goals. Many independent analyses estimate that CCS could supply a significant portion of cumulative global emission cuts needed by mid-century, particularly under scenarios aligned with stabilized temperature outcomes.
Although projections vary, the consensus remains the same: CCS is a crucial element in global decarbonization. The CCS process typically includes:
- Capture: Removing CO₂ from flue gases or industrial streams.
- Transport: Moving compressed CO₂ via pipelines or dedicated vessels.
- Storage: Injecting CO₂ into geological formations such as deep saline aquifers or depleted reservoirs where it can remain safely for centuries.
Because CCS integrates with existing industrial operations, it provides a practical pathway for high-emitting sectors to reduce their environmental footprint without major disruptions to production.
Why Are Carbon Capture & Storage Courses Important for Energy Professionals?
For leaders in energy and heavy industry, understanding CCS is not merely a technical necessity—it’s a strategic advantage. The global push toward emission reduction has created new expectations for how organizations operate, report, and plan.
1. Strategic decision-making requires CCS literacy
Several international industrial analyses have shown that companies incorporating early decarbonization strategies often enjoy cost efficiencies, reduced future compliance risks, and improved resilience. CCS is one of the most impactful tools in that portfolio, and leaders must be equipped to assess how and when to adopt it.
2. Reducing risk in large-scale investments
CCS projects can involve millions in capital expenditure and decades of operational commitments. Leaders who understand the fundamentals—cost curves, geological conditions, regulatory requirements—are better prepared to evaluate feasibility and anticipate risks.
3. Improved cross-functional communication
CCS implementation involves engineering teams, sustainability divisions, finance leadership, regulators, and community stakeholders. Leaders equipped with CCS knowledge can bridge communication gaps and ensure smoother project alignment.
4. Enhanced corporate positioning
A growing body of business and sustainability insights indicates that organizations with strong decarbonization initiatives often see improved investor confidence and stakeholder trust. CCS knowledge empowers leaders to position their organizations as forward-thinking and committed to energy transition goals.
Benefits of Taking Carbon Capture & Storage Courses
A well-designed CCS course equips leaders with both the technical clarity and the strategic understanding needed to guide their organizations through complex transitions.
1. Strengthening technical understanding
Courses help decision-makers understand how capture technologies differ, what geological storage conditions are ideal, and how infrastructure integrates into existing facilities.
2. Supporting long-term strategic planning
Prominent climate research institutions consistently emphasize CCS as part of global pathways toward limiting long-term warming. Leaders trained in CCS are better positioned to design strategies that align with evolving regional and international expectations.
3. Improving capital investment decisions
With training, executives can better evaluate financial models, incentive structures, and lifecycle costs—helping them refine budget allocation and reduce exposure to uncertainties.
4. Enhancing ESG performance
A wide range of business analysis indicates that companies with robust environmental strategies often enjoy competitive advantages. CCS adoption enhances corporate ESG profiles, making companies more appealing to investors and partners.
5. Unlocking new revenue and partnership opportunities
Beyond emission reduction, CCS creates potential business opportunities, such as offering CO₂ transport services, building storage hubs, and forming partnerships with industrial clusters seeking carbon solutions.
What is Carbon Capture & Storage Training Objective?
During this course, you will
- Explore the role of geoscience in CCS and its impact on CO2 emissions reduction.
- Examine past CO2 injection projects and their differences from industrial-scale CCS.
- Understand CO2 behaviour in the subsurface, including injection pressures and stress regimes.
- Learn about CO2 storage capacities, from pore-scale to aquifer volumes.
- Analyse factors influencing CO2 flow, including permeability and aquifer architecture.
- Investigate the effects of CO2 on host aquifers, from geomechanical to geochemical impacts.
- Assess seal integrity and risks, from fracking to induced seismicity and leakage.
- Explore strategies for monitoring and ensuring safe, long-term CO2 storage.
- Compare CCS in saline aquifers versus depleted gas fields.
What are Carbon Capture & Storage Training Outlines?
Day 1 : Overview
- Introductions and Context
– Background on CCS and its role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, with an exercise on - changing greenhouse gas sources in developed nations.
– Geological Storage Options - Overview of CCS history, types of projects, and extend of need to scale up CCS, with a related exercise.
- Evidence and Projects
– Insights into CO2-EOR, saline aquifer CCS, hub and cluster plans, and typical injection rates. - CO2 Properties and Storage
– Phase behavior, trapping mechanisms, and storage quantification in saline aquifers vs. depleted gas fields, with an exercise on phase and depth effects - Porosity in Storage Reservoirs
– Typical values, porosity distribution in sandstones and carbonates - Case study and exercise: Porosity controls in CCS reservoirs.
Day 2
- Storage Efficiency
– Factors influencing CO2 trapping, including viscosity, buoyancy, and plume radius, with a comparison of efficiency in gas fields vs. saline aquifers. Exercise on storage efficiency influenced by (i) fluid viscosity and (ii) gravity effects. - CO2 Injectivity
– Key role of permeability in injection rates, controls on permeability, and an exercise predicting injection rates - Relative Permeability
– Impact on CO2 flow, formation damage, and intraformational baffles, with an exercise on predicting effect of formation damage on injection rates. - Geomechanical Aspects
– Effects of high-pressure CO2 on stresses, fault failure, and intact rock behavior in saline aquifers and gas fields. Exercise on safe maximum CO2 injection pressure and thus injection rates. - Mineral Dissolution Processes
– Mechanisms, extent, and evidence of dissolution, and its effects on storage and injection rates. - Case study and exercise: The range effects of dissolution on CO2 storage and injection rate.
Day 3
- Mineral Precipitation Processes
– Causes, controls, and likely extent of mineral precipitation during CO2 injection, including halite in saline aquifers and rapid mineral sequestration in basalts. - Top-Seal Attributes
– Mudstone porosity, geochemistry, and effects of CO2, with an exercise on calculating maximum safe CO2 column height. - Leakage Risks
– CO2 diffusion and advection through top-seals, leakage via wells, and interaction with well materials. Exercise on predicting potential leakage rates from saline aquifers. - Geomechanical Issues
– Fault behaviour under CO2 pressure, fault reactivation risks, and fracturing evidence. Exercise on predicting uplift from CO2 injection. - Monitoring CO2 Injection
– Purposes, methods, costs, and regulatory requirements, with a focus on risk assessment using immediacy versus severity matrices. - Case study and synthesis comparing the successful Sleipner (Norway) and the terminated In Salah (Algeria) CCS projects in terms of perception of leakage risk
Who Should Attend Carbon Capture & Storage Training?
This course is designed for technical staff, geoscientists, petrophysicists and engineers, most of whom will have had experience in oil and gas exploration and production projects; the course will allow you to adapt your existing petroleum skills for the new world of CCS. The course is also suitable for those from a technical background embarking on a career in the energy transition.
Advance Your CCS Expertise with PetroSync Courses
If you are ready to elevate your leadership capability and guide your organization through decarbonization with confidence, PetroSync offers specialized Carbon Capture & Storage courses tailored for senior professionals. Our programs combine expert-led instruction, real-world case studies, and strategic frameworks designed for decision-makers who need more than just technical understanding—they need clarity for long-term planning.
With PetroSync, you will:
- Understand CCS technologies with practical depth
- Assess regulatory and financial implications
- Strengthen your organization’s decarbonization roadmap
- Lead CCS initiatives with authority and confidence
- CCS expertise is becoming a defining leadership skill. PetroSync is here to support your journey as you shape the future of your organization—and the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) is a set of technologies that capture CO2 emissions from industrial or power-generation sources, transport them, and store them safely underground. CCS is important because it provides a scalable solution to reduce emissions from sectors that are difficult to decarbonize using renewable energy alone.
CCS courses equip energy professionals with the technical and strategic understanding needed to make informed investment decisions, manage long-term risks, support decarbonization strategies, and communicate effectively across engineering, finance, regulatory, and sustainability teams.
Participants will learn about CO2 capture and storage technologies, subsurface CO2 behavior, storage capacity evaluation, injectivity, geomechanics, seal integrity, leakage risks, monitoring strategies, and comparisons between saline aquifers and depleted gas fields.
These courses are designed for geoscientists, engineers, petrophysicists, and technical professionals with oil and gas experience, as well as individuals from technical backgrounds transitioning into energy transition and decarbonization roles.
CCS courses help leaders strengthen ESG performance, reduce regulatory and investment risks, improve capital planning, and identify new business opportunities such as CO2 transport, storage hubs, and industrial partnerships aligned with long-term decarbonization objectives.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.