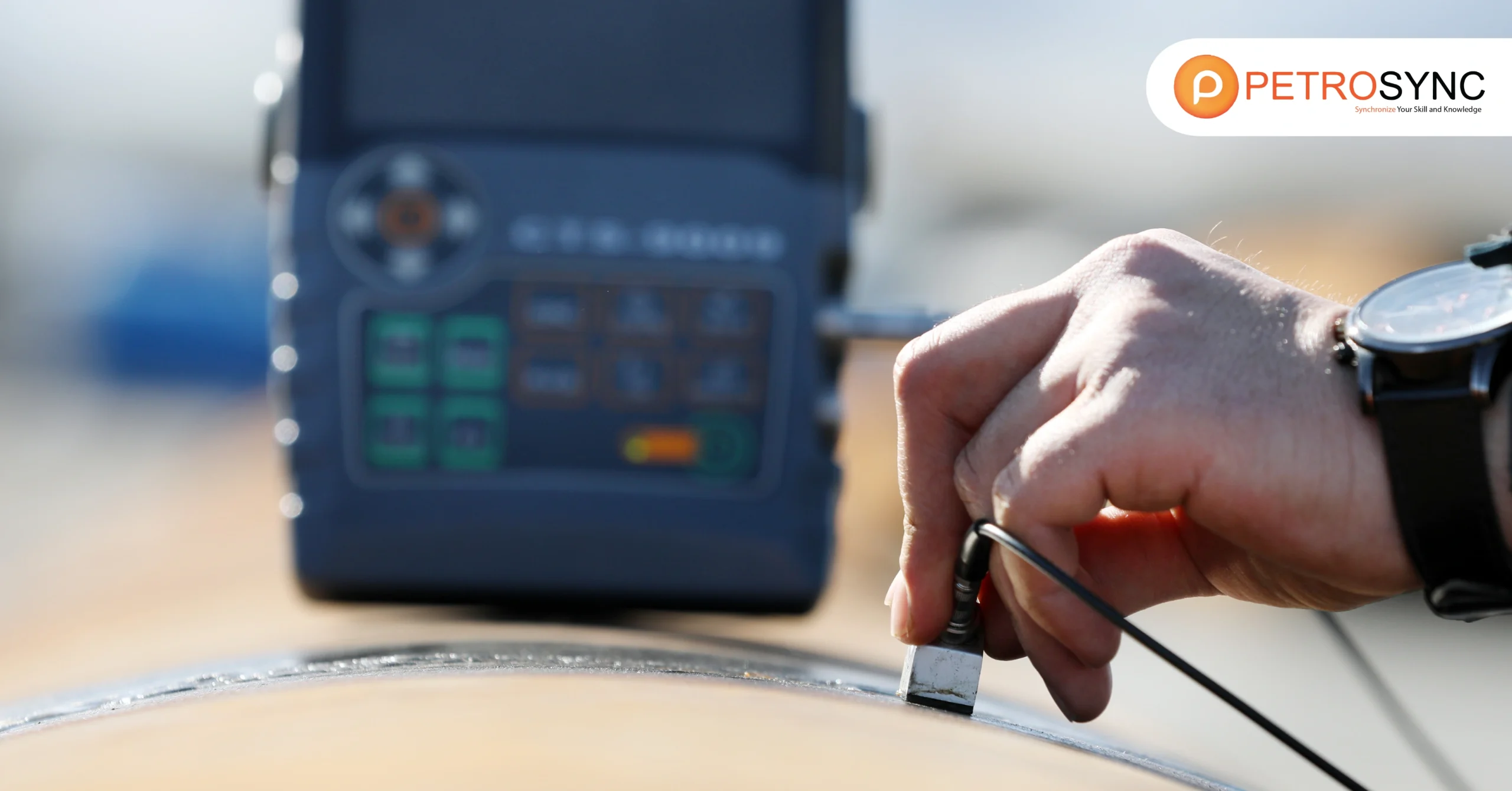
Reliability is now not simply a technical duty however the basis of safety, efficiency, and organisation reputation. This is the place Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) performs a quintessential role. This technique lets in us to look into materials, components, or buildings barring adverse them, making sure non-stop manufacturing and operational processes.
Despite being a fundamental section of present day inspection standards, many specialists nonetheless lack a complete perception of NDT – specially the distinction between NDT and NDE, profession prospects, and the modern-day applied sciences disrupting ordinary approaches.
This article thoroughly explores all of these aspects with a practical approach and up-to-date data relevant for decision-makers in the energy sector.
What Is a Non-Destructive Testing Method?
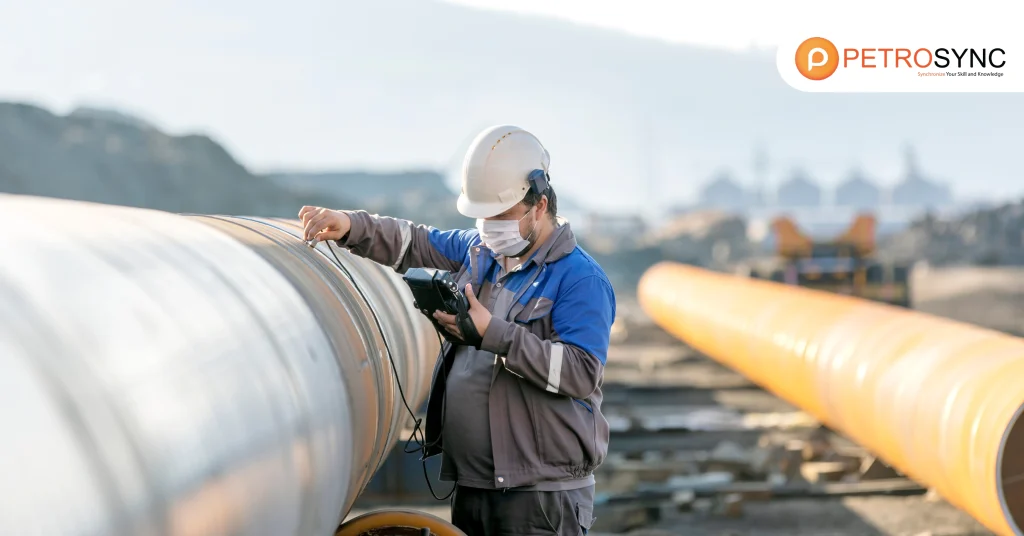

Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a set of techniques used to assess the condition of a material or structure without causing damage. In other words, you can “see inside” metals, pipes, tanks, or weld joints without cutting, dismantling, or stopping operations.
Some of the most commonly used NDT methods in the oil and gas industry include:
Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws.
Uses X-rays or gamma rays to view internal material structures.
3. Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
Suitable for detecting surface cracks on ferromagnetic materials..
4. Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
Effective for exposing small defects such as porosity or fine cracks.
While simple, visual inspection remains an essential first step.
This approach not only extends asset lifespan but also enables teams to respond to potential failures before they escalate into major breakdowns.
What’s the Difference Between NDT and NDE?
The terms NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) and NDE (Non-Destructive Evaluation) are often used interchangeably but technically have distinct meanings.
- NDT focuses on detecting defects.
- NDE encompasses further evaluation of material characteristics such as thickness, strength, or remaining life estimation.
Think of NDT as the problem detector, while NDE is the analysis that follows. In the field, NDT is used to identify damage, and NDE takes the next step to determine its impact and corrective actions.
For senior professionals in engineering sectors, understanding this difference helps in selecting the appropriate inspection method for project needs or certification standards.
Is Non-Destructive Testing a Good Career?
The answer is: absolutely yes, especially in the energy, construction, and heavy manufacturing industries. The demand for certified NDT professionals is increasing steadily. According to Frost & Sullivan, the global NDT market is projected to grow from USD 8.3 billion in 2023 to USD 12.1 billion by 2030.
Why is this profession gaining popularity?
-
Competitive Salaries
In many countries, Level II or Level III NDT Technicians earn salaries comparable to senior engineers.
-
Global Opportunities
Certifications like ASNT, PCN, or ISO open international job opportunities, including in oil and gas zones such as the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
-
Strategic Role
NDT professionals are not just inspection technicians; they become part of risk management, quality control, and project compliance.
-
Sustainable Career
In an era increasingly focused on safety and sustainability, the role of NDT is more vital than ever.
For those aiming to add strategic value to their organization or engineering teams, acquiring NDT knowledge and certification is a highly worthwhile step.
What Is the Latest Technology for Non-Destructive Testing?
Innovation continues to push the boundaries of NDT capabilities. Some of the latest technologies being widely adopted include:
1. Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT)
Utilizes an array of sensors to create real-time internal images of materials, increasing accuracy and speeding up inspections.
2. Digital Radiography (DR)
Replaces traditional film with digital sensors, allowing immediate analysis through software – saving time and being more environmentally friendly.
3. Eddy Current Array (ECA)
Enables detection of surface and subsurface damage without direct contact. Ideal for inspecting piping, tubes, and heat exchanger.
Drone & Robot for Remote NDT Used to inspect high or hazardous areas safely and efficiently, especially useful in offshore or petrochemical plants.
Research and Markets reports that adopting digital technology in NDT can accelerate inspection processes by up to 40% and reduce costs by around 25%. Adopting these technologies is not merely about following trends but a strategic move to improve accuracy, safety, and business efficiency.
Join PetroSync for Industry-Leading Training
If you want to enhance your technical and strategic competencies in NDT, certified training from PetroSync could be the right step. PetroSync offers professional NDT training programs tailored specifically for the energy, construction, and heavy industries sectors. The curriculum is developed by experienced practitioners and aligned with international standards (ASNT, ISO, API).
By attending this training, you will:
- Gain practical understanding of various NDT methods
- Develop skills relevant to the latest technologies
- Prepare for international certification
- Increase your competitiveness and value in the global market
Don’t wait for risks to appear before taking action. Invest in your skills now for a safer and more productive future.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.