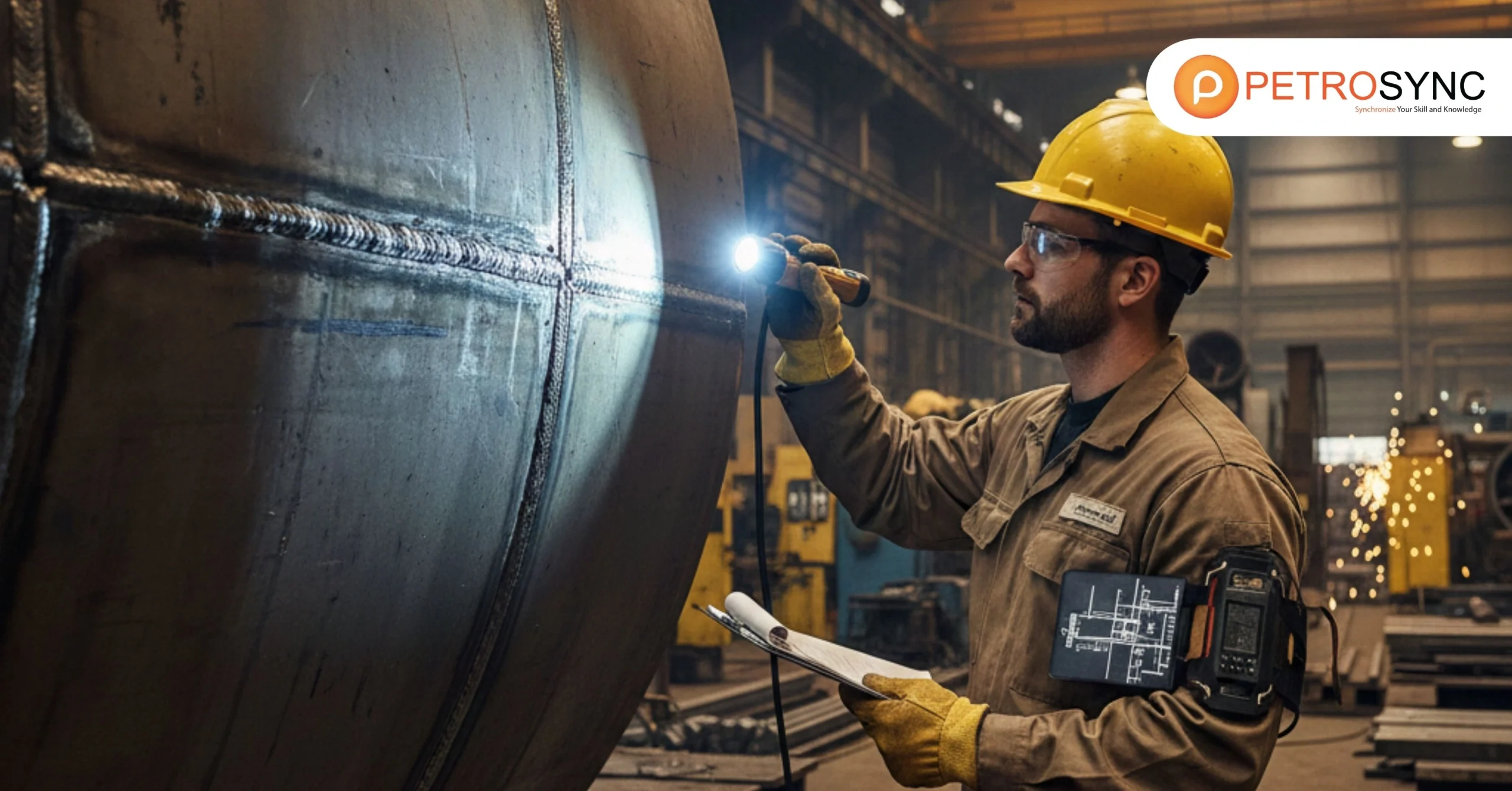
ASME Section VIII Division 1 is one of the most essential global engineering standards governing the safe design, fabrication, inspection, and certification of pressure vessels used across critical industrial sectors. From oil and gas production, petrochemical processing, and power generation to pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Pressure vessels operate under extreme pressure and temperature conditions where even small design or inspection errors can lead to catastrophic consequences. History has shown that pressure vessel failures have resulted in industrial explosions, severe injuries, extended operational shutdowns, and multimillion-dollar asset losses.
Therefore, professionals must actively understand and apply ASME Section VIII Div 1 to protect human life, ensure asset reliability, and maintain business continuity—making it not just compliance, but a strategic responsibility.. Engineering leaders who master this standard ensure that operations remain safe, efficient, and aligned with best global practices.
Let’s first understand why this standard is foundational for pressure vessel safety before we explore how ASME Section VIII Div 1 applies in real industrial environments.

ASME Section VIII Division 1 is a set of rules and standards established by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). Section VIII, Division 1 deals with regulations about the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels of pressure vessels that operate under internal or external pressures surpassing 15 pounds per square inch gauge (psig). These vessels could be either fired or unfired.
This set of rules published by ASME helps engineers and manufacturers make pressure vessels by providing clear instructions and standards to ensure their reliability and safety.
In Section VIII, Division 1, you’ll find various appendices, some required and others optional. These appendices provide additional guidelines for designing pressure vessels, explaining nondestructive examination methods and standards for accepting inspections. The section also outlines rules for using the ASME certification mark with the U, UM, and UV designators.
What Is The Difference between ASME VIII Div 2 and Div 1?
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) establishes two distinct sets of rules—ASME Section VIII Division 1 and Division 2—to guide the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels. In essence, division 1 relies on the normal stress theory, whereas Division 2 utilizes the maximum distortion energy principle (Von Mises).
Division 1 primarily applies to a broad range of pressure vessels, providing general requirements for their design and construction. It covers vessels operating at pressures above 15 pounds per square inch gauge (psig), both for internal and external pressures. Division 1 is commonly used for standard applications and is more straightforward in its approach.
On the other hand, Division 2 is more specialized and offers an alternative set of guidelines specifically suited for pressure vessels with higher complexity. It is often chosen when the design involves unique conditions or materials. Division 2 takes a more detailed and in-depth approach to the analysis and design of pressure vessels, providing a more rigorous framework for situations where Division 1 might not offer sufficient guidance.
In essence, the key difference lies in the scope and complexity of the pressure vessel design. Division 1 covers common cases; Division 2 handles complex designs. Engineers choose based on project requirements for safer pressure vessels.
What Are The Key Changes in BPVC Section VIII, Division 1 (ASME BPVC-VIII-1)?
Some of the notable changes in ASME Section VIII Div. 1 are:
1. Impact Test Requirements for Diffusion Welding (DFW)
A new paragraph, UG-84(d)(3), has been added to articulate the impact test requirements specifically for diffusion welding (DFW). This addition aims to provide precise guidelines and enhance clarity in this aspect of pressure vessel fabrication.
2. Sharing of Proof Testing Reports
The introduction of Paragraph UG-101(a)(5) addresses the sharing of proof testing reports among manufacturers owned by the same entity. This inclusion ensures a standardized and transparent approach to proof testing within affiliated manufacturing entities.
3. Consistency in Heat Exchanger Types (Part UHX)
Part UHX has undergone significant realignment and revision to ensure consistency among different heat exchanger types. The revision involves basing the shell and channel coefficients on the mean diameter instead of the inside diameter, aligning with the principles outlined in PTB-7.
4. Streamlining Heat Exchanger Design Rules
Part UHX and Appendix 26 design rules, identical to Part 4.18 and 4.19 of Division 2, have been removed. Instead, they now refer to Part 4.18 and 4.19 when applicable, streamlining the design requirements for all heat exchangers. This modification facilitates easier maintenance through a unified set of rules.
5. Global Designator Update – “PRT” to “PRT VIII-1”
A global change has been implemented throughout Section VIII, Division 1, updating the “PRT” designator to “PRT VIII-1”. This standardized labeling system ensures consistency across the entire section.
What Is ASME Section VIII Division 1 Appendix 46?
Division 1 of ASME Section VIII doesn’t cover all the details of pressure vessel design. When specific rules are lacking, U-2(g) allows alternatives, including using Mandatory Appendix 46.
This appendix outlines how to incorporate Section VIII, Division 2 rules into the design of Division 1 pressure vessels, with restrictions outlined in five categories:
- Allowable Stresses
- Design Thickness and Weld Joint Efficiency,
- Design Loads and Load Case Combinations,
- Weld Joint Details, and
- Fabrication Tolerances
Appendix 46 allows using Division 2 for Division 1 vessel design, but with limits due to differing material, design, and fabrication requirements. Division 2 offers two design methods:
- Design by Rule (formulas for components)
- Design by Analysis (requirements for numerical analysis).
Adhering to the restrictions outlined is crucial for ensuring a seamless application of Division 2 rules in the design of Division 1 pressure vessels.
What Is ASME Section VIII Divisions 1 Appendix 47?
ASME Section VIII 2021 added Appendix 47 defining pressure-vessel design roles and responsible-charge oversight per NSPE Statement 1778. Designer and engineer requirements differ by experience, education, and licensing, with manufacturers providing alternative minimum experience options. Additionally, Appendix 47 outlines extra qualifications for certain design activities, such as:
- Performing numerical analyses (such as finite element analysis)
- Conducting fatigue assessments
- Design for seismic reactions (specifically response history procedure)
- Design of quick-actuating closures
- Performing design activities not specifically addressed by Section VIII, Division 1.
In summary, ASME Section VIII, Division 1 is a foundational standard in pressure vessel design. It offers clear guidelines for creating, inspecting, and certifying these vessels, ensuring their safety and reliability. This code is widely embraced across industries, providing a common set of practices that engineers and manufacturers follow.
ASME Section VIII Div 1 enhances safety, ensures compliance, boosts efficiency, and standardizes engineering practices in pressure vessel operations.
Join PetroSync Training to Enhance Your Professional Skills
PetroSync provides comprehensive training covering both ASME Section VIII, Division 1 and Division 2, offering you a thorough understanding of pressure vessel design. By enrolling in PetroSync’s ASME Section VIII training, you enhance your expertise in industry-standard practices and gain versatility to navigate diverse scenarios.
We commit to ensuring you can stay relevant, and equipped with in-depth knowledge and the latest advancements in pressure vessel technology. Choosing PetroSync should be your investment in professional growth, empowering you to excel in the dynamic field of pressure vessel engineering.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.