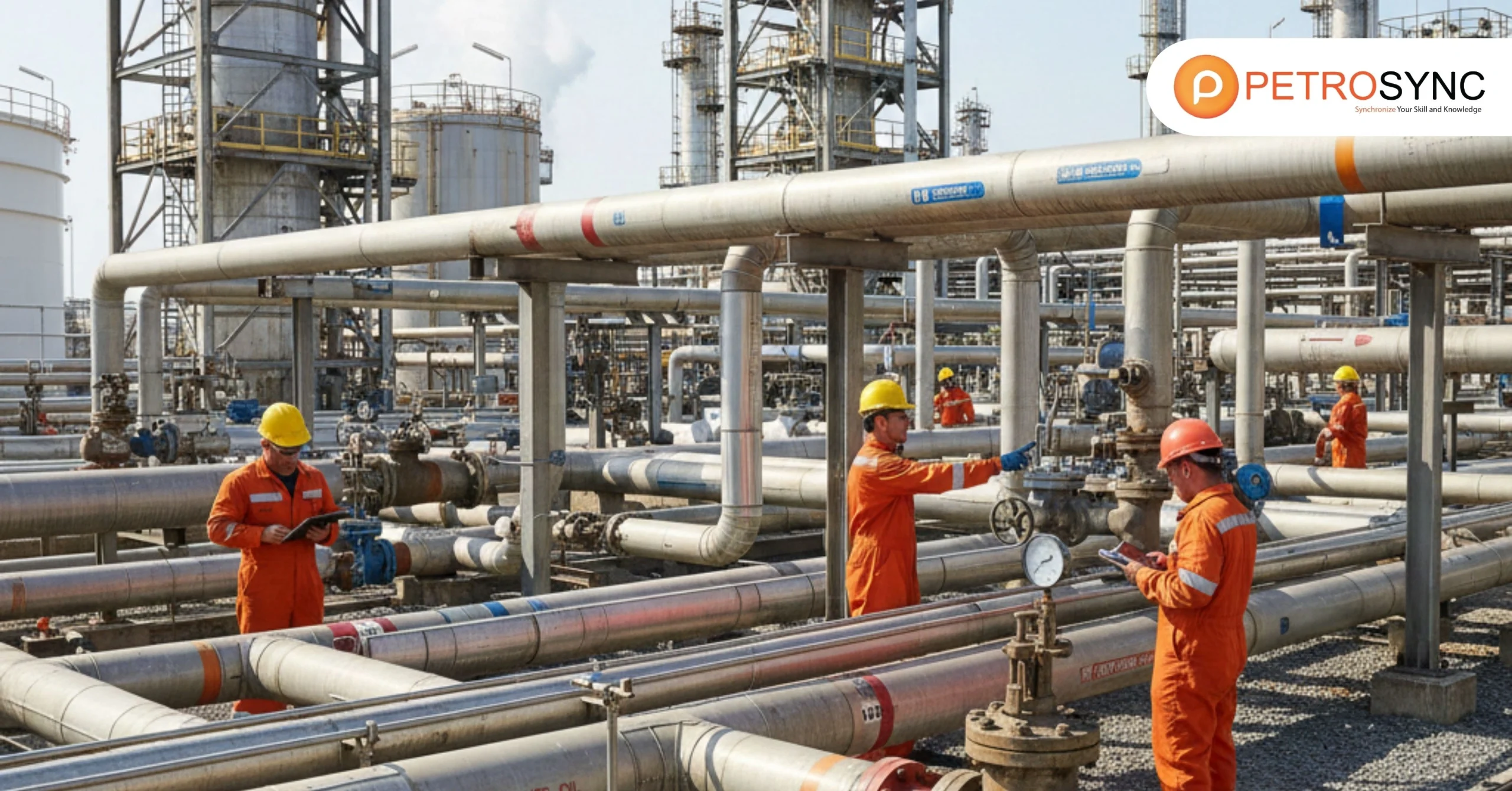
Piping class plays a critical role in ensuring safe and reliable operations in the oil and gas industry. Even a minor misstep in piping design can lead to serious safety incidents, environmental risks, or costly operational shutdowns. Implementing the correct piping class not only reduces operational risks but also enhances reliability, efficiency, and long-term asset integrity.
By understanding piping class in detail, organizations can optimize maintenance strategies, support compliance with industry standards, and maintain safer operations. For senior engineers, managers, and executives, mastering piping class is essential to effectively lead modern oil and gas facilities.
Why Piping Class is Essential to Protect Safety in Oil & Gas Operations
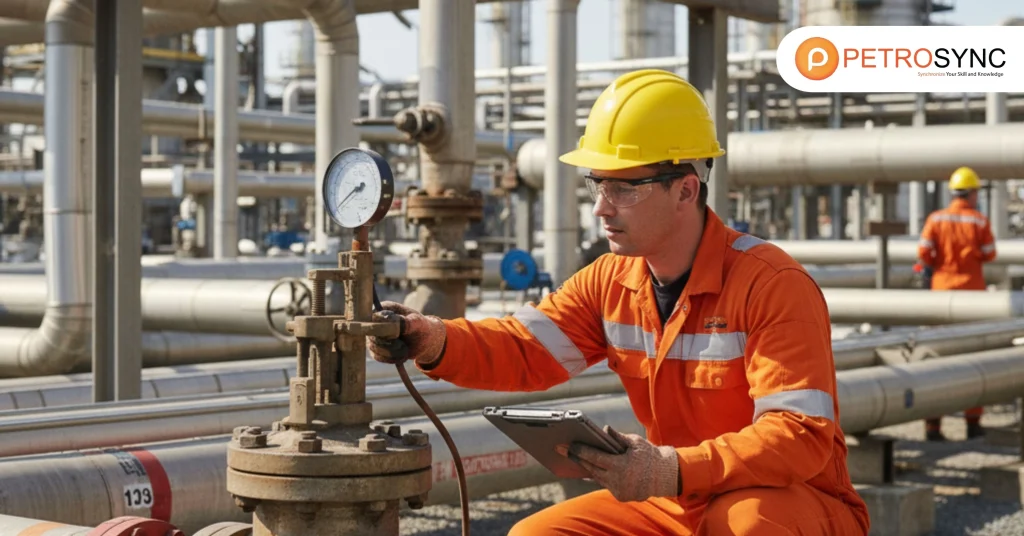

Pipelines are the lifelines of oil and gas facilities, carrying high-pressure, high-temperature fluids between processing units. Any failure in these pipelines — from leaks to ruptures — can have catastrophic consequences, including environmental damage, production loss, and even safety incidents.
Piping class ensures that each segment is designed, fabricated, and maintained to withstand operational stresses safely. Without proper classification, sections may be under-designed or specified incorrectly, leaving them vulnerable to fatigue, corrosion, vibration, or overpressure.
Industry experience indicates that mechanical fatigue and corrosion are among the leading causes of piping failures, often preventable with proper design and classification. Proper piping class integration also supports pipeline integrity programs by prioritizing high-risk areas, guiding inspections, and enabling preventive maintenance. Facilities that adopt these practices consistently achieve safer, more reliable operations.
What Is a Piping Class? Understanding Its Structure, Purpose & Technical Elements
A piping class defines the technical criteria for materials, dimensions, and components used in a piping system. It serves as a blueprint to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance.
1. Pipe material grade, corrosion allowance & wall thickness
Material selection is the first step in determining a piping class. Fluids with different chemical properties, such as sour gas or hydrocarbons, require materials that resist corrosion and maintain integrity under temperature and pressure stresses.
A corrosion allowance is added to compensate for expected material loss over time. Wall thickness is calculated to balance durability and cost efficiency, ensuring pipes withstand operating pressures and environmental conditions without overdesigning.
2. Pressure–temperature rating (ASME standards)
The pressure–temperature rating determines which piping class is suitable for specific operating conditions. Standards such as ASME B31.3 provide guidelines for assigning classes based on process temperature and pressure. Proper ratings prevent overpressure incidents and ensure safe operation, supporting hydrostatic and non-destructive testing protocols.
3. Specifications for valves, flanges, gaskets, bolts & testing
Piping class extends beyond the pipe itself. It specifies:
- Valves and flanges: Must meet or exceed class ratings to avoid weak points.
- Gaskets and bolts: Must tolerate thermal expansion, pressure cycles, and vibration.
- Testing protocols: Hydrostatic, pneumatic, and non-destructive testing validate component integrity before commissioning.
This comprehensive approach ensures that every part of the piping network performs reliably under operational conditions.
How the Right Piping Class Improves Reliability, Safety & Operational Efficiency
Correct piping classification has direct benefits beyond regulatory compliance.
1. Prevents leaks, ruptures & catastrophic failures
Proper material selection, corrosion allowance, and pressure ratings minimize the risk of leaks, ruptures, and fatigue failures. By adhering to classification guidelines, facilities can prevent costly downtime and ensure safer operations.
2. Reduces maintenance costs & increases plant uptime
Well-specified piping reduces unexpected failures, enabling planned, strategic maintenance. Risk-based inspection programs can then target high-priority areas, minimizing downtime and operational disruption. Facilities applying these methods report lower maintenance costs and higher uptime, supporting ROI-driven decision-making.
3. Supports compliance & asset lifecycle integrity
Piping class helps meet regulatory requirements and industry standards while enabling long-term lifecycle management. Correct classification informs inspection schedules, fitness-for-service evaluations, and risk-based maintenance, ensuring assets remain safe and productive throughout their service life.
Who Needs to Master Piping Class to Lead Modern Oil & Gas Operations?
Understanding piping class is essential for multiple roles in oil and gas operations.
1. Piping, Mechanical, Integrity & Project Engineers
Engineers involved in design or project execution must understand piping class to select materials, determine wall thickness, and assign pressure ratings. This expertise prevents overdesign, reduces costs, and ensures system safety.
2. Operations, Maintenance, QA/QC & HSE Teams
Operations and maintenance teams rely on class knowledge to guide inspections, monitor system performance, and conduct preventive maintenance. QA/QC personnel ensure that components meet required standards, while HSE teams benefit from reduced risk exposure.
3. Asset Management & Reliability Leaders
For asset managers and reliability engineers, piping class data is vital for risk-based inspection planning, lifecycle management, and long-term integrity decisions. Correct classification ensures maximum value from capital and operational investments.
Advance Your Expertise with PetroSync — The Most Practical Piping Class Training
Mastering piping class is not only theoretical but also strategic for operational excellence. PetroSync’s Piping Class for Safer Operations training equips senior leaders, engineers, and HSE professionals with actionable knowledge.
Key benefits include:
- Real case studies: Analyze fatigue cracking, corrosion under insulation, and overpressure incidents to learn preventive strategies.
- Hands-on exercises: Practice material selection, corrosion allowance, wall thickness, and pressure-temperature rating calculations.
- Integration with integrity programs: Learn how class definitions feed into risk-based inspection, lifecycle management, and fitness-for-service evaluations.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Work alongside peers from engineering, operations, maintenance, and HSE to build shared understanding.
This training strengthens safety leadership, reduces operational risk, and improves reliability. Organizations investing in piping class expertise often report measurable improvements in operational uptime, maintenance cost reduction, and extended asset life — delivering clear ROI.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.