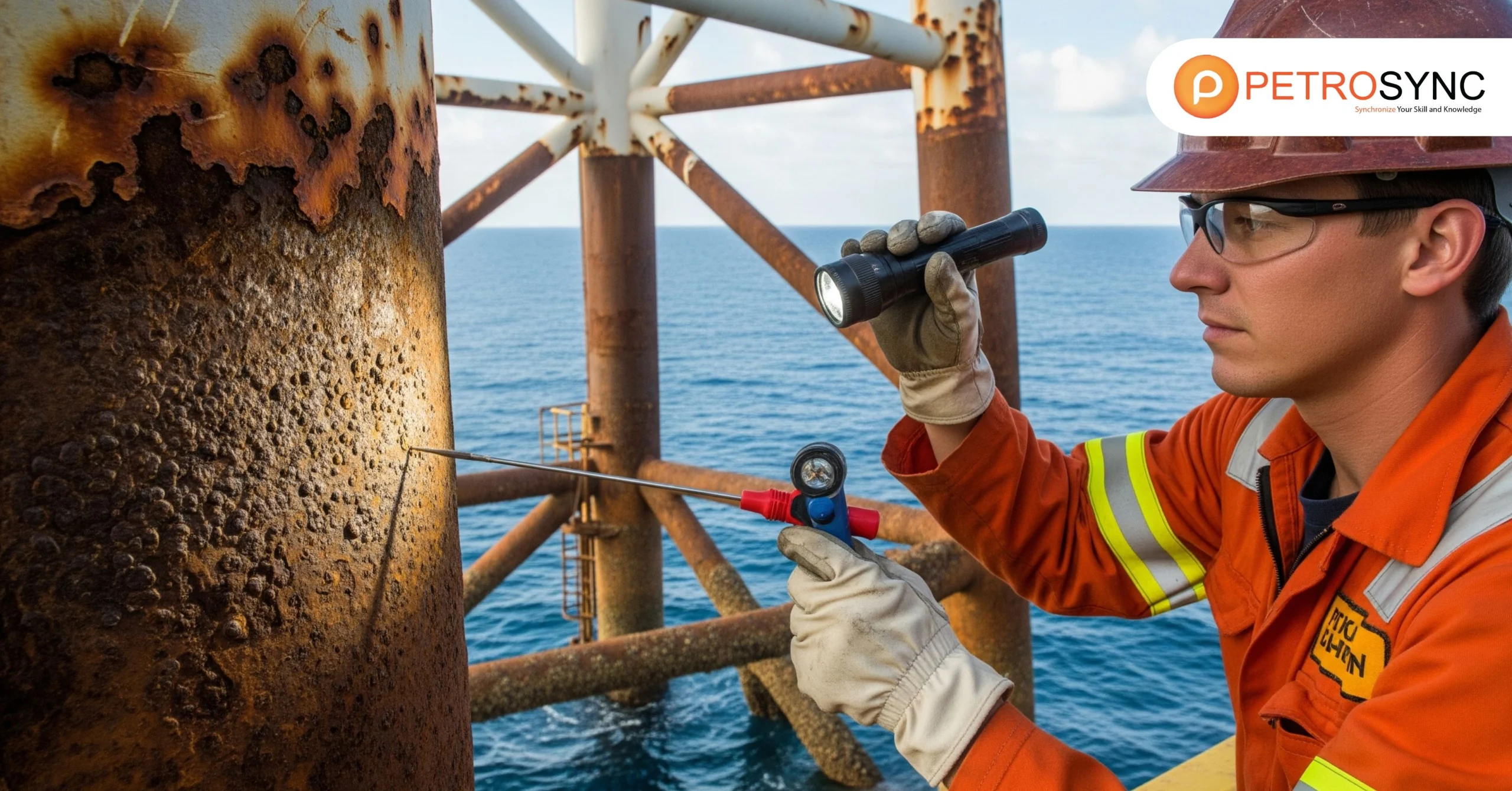
Pitting corrosion is one of the most challenging forms of metal degradation in industrial operations. Its localized nature allows it to silently compromise structural integrity, often without visible signs, making early detection difficult and increasing the risk of sudden equipment failure.
Industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine operations are particularly vulnerable, where operational downtime and safety incidents can lead to significant financial and reputational losses. Understanding the mechanisms of pitting corrosion and implementing effective prevention strategies is therefore crucial for maintaining asset reliability, ensuring workplace safety, and protecting long-term investments.
This article explores what pitting corrosion is, why it poses a critical concern, and the most effective solutions and best practices for managing it over the long term.
What is Pitting Corrosion?
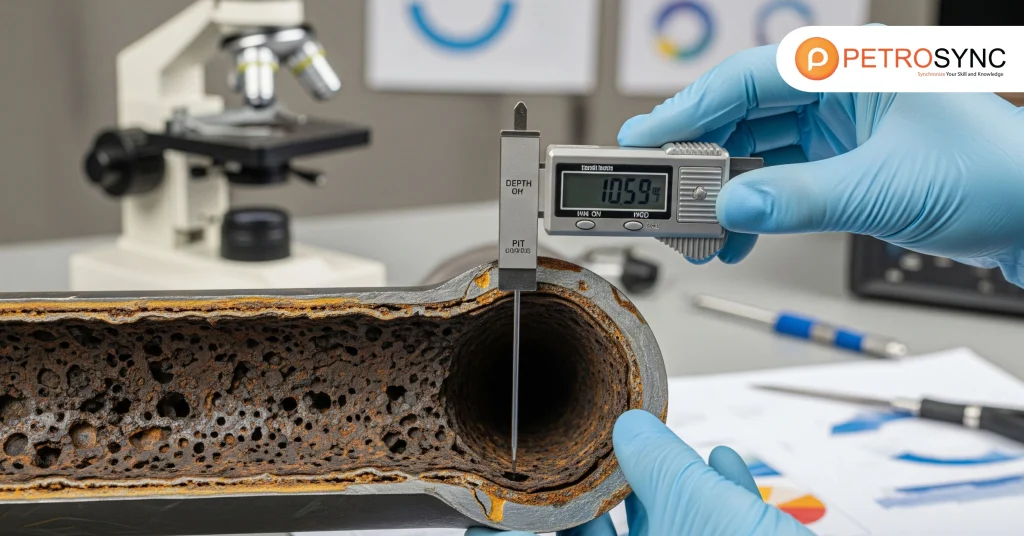

Pitting corrosion manifests as small, localized holes on metal surfaces. Initially microscopic, these pits can deepen over time, undermining structural integrity. Unlike general corrosion, which gradually erodes surfaces, pitting occurs in concentrated spots—often under coatings, welds, or crevices—where aggressive ions accumulate.
Its danger lies in its stealth. Deep pits may form without visible signs, increasing the risk of catastrophic failure. Studies from industrial corrosion experts indicate that pitting can reduce load-bearing capacity of pipelines by 20–30% if left unchecked, highlighting the importance of early mitigation strategies.
Why Pitting Corrosion is a Critical Concern for Industrial Safety
Pitting corrosion can silently weaken structures, ultimately leading to leaks, ruptures, or even accidents. Historical incidents, like the Silver Bridge collapse in 1967, demonstrate how localized corrosion contributes to structural failure. In modern industries, pipelines and storage tank in oil and gas environments face constant exposure to saline water and chemicals, accelerating pit formation.
Research shows that proactive corrosion management can reduce failure incidents by nearly 40%, proving that timely detection and prevention are essential for safety, operational continuity, and regulatory compliance.
Solutions for Pitting Corrosion Prevention
1. Material Selection and Protective Coatings
Selecting corrosion-resistant materials is the first defense. Stainless steels with high chromium and molybdenum, titanium alloys, and nickel-based materials are particularly effective. Molybdenum stabilizes the passive oxide layer, increasing resistance to chloride-rich environments.
Protective coatings, such as thermal spray or epoxy layers, act as physical barriers. Combined material and coating strategies can extend equipment lifespan by 25–35%, making them a cost-effective long-term investment.
2. Regular Inspection and Monitoring Techniques
Routine inspections are critical. Techniques like ultrasonic testing, eddy current evaluation, and visual inspection can detect early-stage pits. Advanced AI-driven monitoring systems now allow real-time detection, improving early intervention capabilities.
Case studies in offshore pipelines show that structured inspection programs can identify over 90% of pitting formations before they result in failure, significantly improving asset safety.
3. Corrosion Inhibitors and Chemical Treatments
Corrosion inhibitors provide a chemical shield on metal surfaces, preventing aggressive ions from initiating pits. In industrial pipelines, inhibitors such as amines or phosphates are routinely used. Studies demonstrate that well-managed inhibitor programs can reduce pit growth rates by up to 60%, highlighting their effectiveness in operational reliability and cost control.
4. Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) Programs
RBI prioritizes inspections based on likelihood and consequences of failure. By focusing resources on the most critical assets, organizations reduce unnecessary costs while enhancing safety. Industry guidelines show that RBI-based inspection programs improve decision-making and extend asset lifespan, ensuring proactive rather than reactive management.
Best Practices for Long-Term Pitting Corrosion Management
1. Integrated Asset Integrity Management
Combining maintenance, engineering, and operational data ensures a holistic approach. Integrated programs have been shown to extend equipment life by up to 20%, improving overall reliability while optimizing maintenance budgets.
2. Continuous Training and Knowledge Development
Regular training keeps personnel updated on latest techniques and risk factors. Surveys show that organizations investing in continuous corrosion training experience 30% fewer equipment failures related to pitting.
3. Compliance with Industry Standards and Guidelines
Adherence to established standards such as NACE MR0175, ASTM G48, and API RBI ensures effective and consistent corrosion prevention, reducing operational and regulatory risks.
Strengthening Equipment Safety Through Proactive Pitting Corrosion Management
By adopting proactive strategies, organizations can:
1. Ensure Operational Continuity and Reliability
Timely inspections and interventions prevent unexpected failures, reducing costly downtime.
2. Protect Investments and Reduce Downtime
Preventive measures minimize repair needs, safeguarding financial investments and production output.
3. Enhance Safety Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Proactive corrosion management mitigates operational risks, ensuring safer working conditions and regulatory compliance.
Advance Your Pitting Corrosion Management Expertise with PetroSync Training
For professionals seeking to deepen expertise in corrosion management, PetroSync offers specialized training programs. These courses cover advanced pitting corrosion prevention techniques, inspection methods, and risk-based management strategies.
Participants gain actionable knowledge to improve asset integrity, reduce operational risks, and enhance safety compliance. Organizations that applied learnings from PetroSync training have reported measurable improvements in equipment reliability, reduced downtime, and enhanced operational safety—demonstrating a tangible return on professional development investment.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.