In industrial settings, causal factors refer to the factors that contribute to a specific outcome. Recognizing these factors is vital for industries to identify the root cause of problems and take measures to address them. Understanding and resolving causal factors is an essential part of maintaining a prosperous and sustainable industry. In this article, we will discuss the basic, examples, charting, and ways of finding the causal factors.
What Is a Causal Factor?
Causal factors are significant, unplanned, and unintended contributors to an incident (a negative occurence or unwanted condition), that, if removed, would have either prevented the incident entirely or reduced its severity and frequency.
Meanwhile, the US Department of Energy explains that a causal factor is a term used to describe various factors associated with either human performance or a safety management system. It encompasses direct, root, and contributing causes that can be identified by breaking it down into its parts.
To determine the causal factors of an event, a thorough analysis of the preceding circumstances and factors is necessary. Identifying the causal factors can assist in developing effective strategies to prevent similar events from occurring in the future.
What Is The Difference between A Causal Factors and A Root Cause?
|
Causal Factors |
Root Causes |
| Immediate and apparent | Underlying and concealed |
| Contribute to the advancement or worsening of a problem or matter | Represent the systemic factors behind the existence of the problem or issue |
| Can be dealt with more readily and swiftly | Demand deeper analysis and comprehension |
| May not be the principal cause of the matter | Serve as the primary cause of the issue |
| Often clear to identify | Frequently necessitate more investigation and diagnosis |
What Are Causal Factor Examples?
One example of causal factors is when pipeline ruptures may occur for various reasons. A faulty electrical wiring system could cause a fire in a building. In this scenario, the faulty electrical wiring system is the direct cause of the fire. The root cause of the faulty wiring could be a lack of maintenance or inspection of the wiring system.
Contributing causes could be the age of the building, the type of wiring used, or improper installation. By identifying these causal factors, steps can be taken to prevent similar fires from occurring in the future, such as conducting regular maintenance and inspection of electrical systems in buildings.
Another specific example in the oil and gas industry is a pipeline rupture that may occur due to corrosion or damage to the pipeline, which can be caused by inadequate maintenance or inspection.
The pipeline’s age, the material used, and environmental factors such as soil composition or weather conditions may also contribute to the issue. Identifying these causal factors is crucial in developing effective preventive measures, such as implementing a comprehensive maintenance and inspection program, using more durable materials, or altering the pipeline’s route to avoid areas prone to environmental factors that can damage it.
How To Find A Causal Factor?
To identify the causal factors of an incident or event, a thorough investigation needs to be conducted. This involves gathering information about the event, including what happened, when and where it occurred, and who was involved.
Some of the common methods and techniques used to identify causal factors include:
1. Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a methodical approach to identifying the underlying causes of an incident or problem by asking a series of “why” questions until the root cause is identified.
2. Fishbone Diagram
Fishbone diagram is also known as an Ishikawa diagram, it is a visual tool that helps to identify potential causes of a problem by categorizing them into different categories such as people, process, equipment, environment, etc.
3. CLC Analysis
This method identifies causal factors by analyzing the life cycle of an event or problem in chronological order, identifying key events and factors, analyzing causes, and developing preventive measures based on the root causes.
4. 5 Whys Technique
This technique involves asking “why” questions five times to identify the root cause of a problem.
Identifying causal factors requires a systematic and methodical approach, as well as a willingness to investigate the deeper underlying causes beyond the surface-level factors.
What Is Causal Factor Charting?
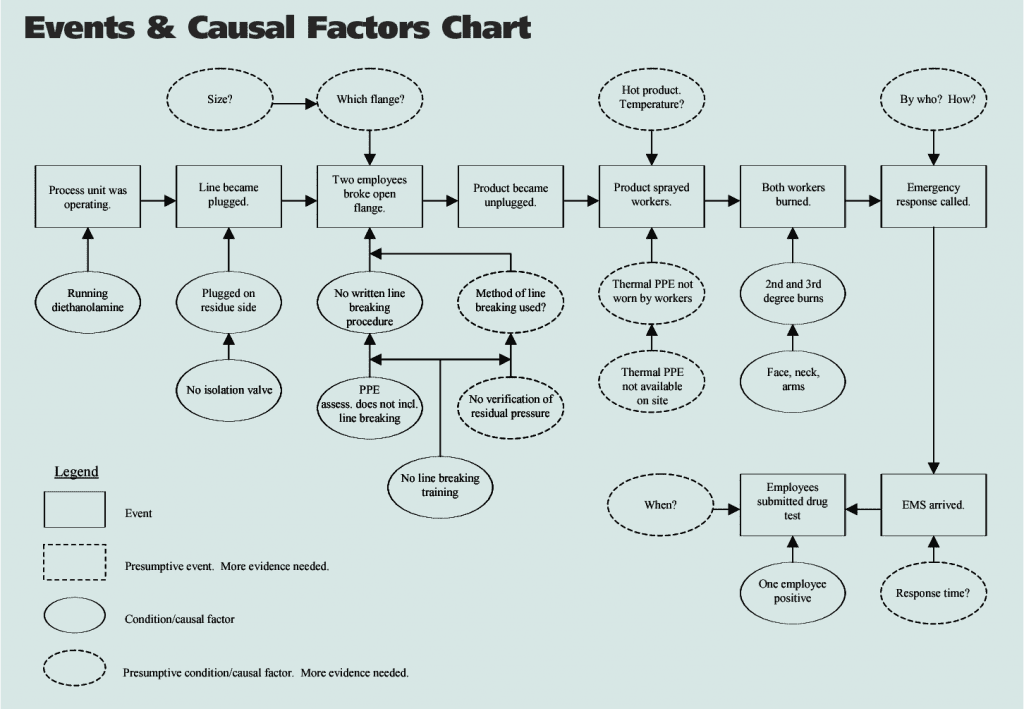
Causal factor charting, which is also known as fault tree analysis, involves creating a flowchart or diagram that starts with the incident or event and works backward to identify the root causes and contributing factors.
Causal factors charting becomes a methodical approach to root cause analysis that visually maps out the causal factors of an incident or event in a structured way.
How to Use Causal Factor Charting?
Causal Factor Charting is used during the RCA process to pinpoint and assess the elements that played a role in an occurrence. The following are the procedures for implementing Causal Factor Charting:
1. Defining Issue
Define the issue by clearly defining the problem or incident that requires analysis.
2. Identifying Outcomes
Identify the outcome by determining the event or outcome that resulted from the incident.
3. Determining Direct Cause
Determine direct causes by identifying the primary factors that led to the event using evidence such as witness statements and data analysis.
4. Identifying Contributing Factors
Identify contributing factors by determining the underlying factors that led to the direct causes, including external factors, human error, or system failures.
5. Creating a Causal Factor Chart
Create the causal factor chart by using the identified factors to construct a causal factor chart in the form of a tree diagram, starting from the event and working backward to identify root causes and contributing factors.
6. Analyzing The Chart
Analyze the chart by studying the causal factor chart to determine the relationships between the factors and to pinpoint the root causes of the incident.
7. Developing Preventive Measures
Develop preventive measures based on the root causes identified in the causal factor chart, and devise measures to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
In the Root Cause Analysis (RCA) process, Causal Factor Charting is a crucial tool that the RCA team can use to identify and analyze the factors that caused an incident. By identifying the causal factors, the involved team can then determine the root cause or causes of the incident and develop effective corrective actions that address the underlying problems. This approach helps to prevent future incidents and improve overall safety performance.
PetroSync’s Root Cause Analysis training course equips attendees with the skills and techniques necessary to identify and analyze the underlying causes of incidents rather than just treating the symptoms. By crafting a thorough course outline, we believe you can gain a deeper understanding of how incidents occur and how to implement preventive measures to ensure your workplace remains safe. So, invest in Root Cause Analysis training today and avoid failure using the best incident investigation with PetroSync!
Credit header image: Freepik.com

SEO specialist by day, fact-checker by night. An avid reader and content writer dedicated to delivering accurate and engaging articles through research and credible sources.







