API 510 is standard is one of the widely used standards with a broad scope in the field of industrial safety and equipment management. In this article, you will delve into the detailed scope of API 510, which encompasses essential aspects such as pressure vessel inspection, assessment criteria, and risk-based inspection concepts.
What Is API 510?
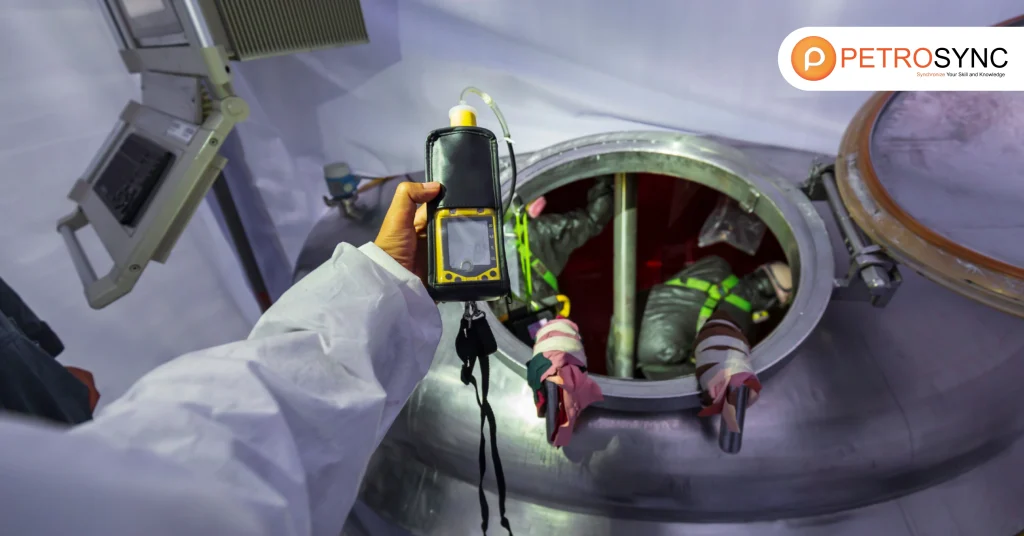
API 510, also known as the “Pressure Vessel Inspection Code: In-Service Inspection, Rating, Repair, and Alteration,” is a certification and standard related to pressure vessel inspection. It outlines the requirements and guidelines for inspecting, repairing, and maintaining pressure vessels used in various industries like oil and gas, petrochemicals, and manufacturing. This certification ensures that pressure vessels are regularly checked to prevent accidents and maintain their safety and operational efficiency.
What is API 510 Standard?
API 510, often known as the Pressure Vessel Inspection Code, is an American Petroleum Institute standard that governs the maintenance, inspection, and repair of pressure vessels. It is especially significant for pressure vessels in the oil, gas, petrochemical, and energy industries, where high-pressure systems require skilled management.
This standard requires pressure vessels to be inspected on a regular basis for evidence of wear, corrosion, or structural flaws that could cause an accident or operational failure. The standard is widely recognized throughout industries, ensuring that enterprises adhere to both regulatory requirements and high safety standards for pressure equipment.
What is The Requirement For API 510?
To comply with API 510, enterprises must develop a complete inspection, maintenance, and repair program for pressure vessels. This includes creating a routine inspection schedule, carrying out nondestructive testing (NDT), and ensuring that only certified inspectors do these evaluations.
Specific training and experience are required for certification, and inspectors must pass an exam to certify compliance with API 510 criteria. Furthermore, the standard requires firms to adequately document all inspection and repair activities in order to ensure traceability and safety precautions. Failure to achieve these requirements can lead to compliance issues, safety concerns, and possible operational downtime.
What are The Benefits of API 510?
Adherence to API 510 offers numerous major benefits, particularly in high-risk businesses. To begin, it improves safety by identifying and resolving hazards early on, therefore protecting both personnel and equipment. Routine API 510 inspections also improve equipment reliability and extend the life of pressure vessels, saving downtime and maintenance costs by detecting any defects early.
Furthermore, following API 510 standards enables businesses to meet regulatory duties, reducing the danger of legal ramifications and fostering continuous, uninterrupted operations. API 510 compliance ensures unparalleled dependability in companies that value time.
What Are The Scope of API 510 – Pressure Vessel Inspection?
The scope of API 510 covers aspects such as inspection procedures, qualifications for personnel conducting inspections, and requirements for assessing the condition of pressure vessels.
General Application of API 510
1. Coverage
The scope of API 510 in its general application coverage is comprehensive and includes various aspects of pressure vessel inspection, repair, alteration, and rerating activities. This inspection code applies to all refining and chemical process vessels that have been placed in service, except for specific exclusions as per section 1.2.2. Here are the key points covered by API 510:
A. Types of Vessels Covered
- Vessels constructed in accordance with an applicable construction code.
- Vessels constructed without a construction code (non-code), meeting no known recognized standard.
- Vessels constructed and approved as jurisdictional special based upon jurisdiction acceptance of particular design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and installation.
- Non-standard vessels, which are vessels fabricated to a recognized construction code but have lost their nameplate or stamping.
B. Relation to ASME Code
- While the ASME Code and other construction codes primarily focus on new construction, API 510’s technical requirements for design, welding, non-destructive examination (NDE), and materials are applicable to the inspection, rerating, repair, and alteration of in-service pressure vessels.
- In cases where an item cannot follow the ASME Code due to new construction orientation, API 510’s requirements for design, material, fabrication, and inspection take precedence.
- If in-service vessels are covered by both ASME Code and API 510 requirements or if there is a conflict between the two codes, the requirements of API 510 shall take precedence.
2. Intent
The scope of API 510 is specific to owner/users who have access to technically qualified individuals and organizations:
- Authorized Inspection Agency: These are organizations authorized to conduct inspections as per API 510 standards.
- Repair Organization: Entities responsible for repairing pressure vessels in compliance with API 510 requirements.
- Engineer: Qualified engineers who provide technical expertise related to pressure vessels.
- Inspector: Certified inspectors who conduct inspections as per API 510 guidelines.
- Examiners: Individuals skilled in examining pressure vessels according to API 510 standards.
It is important to note that inspectors must be certified as outlined in API 510 Appendix B. While there are other codes like NB-23 covering various industries and service applications, API 510 specifically caters to the needs of the refining and petrochemical industry for vessels and pressure-relieving devices within its defined scope.
3. Limitation
The scope of API 510 in its general application limitation is straightforward. It is important to note that while adopting and using this inspection code, you must comply with existing regulatory requirements. If there are any conflicts between this code and prevailing regulations, the regulations take precedence.
However, if this code has stricter requirements than the regulations, then you must follow the code’s requirements for inspection, rating, repair, and alteration of pressure vessels.
Specific Applications of API 510
1. Exploration and Production Vessels
The scope of API 510 in its specific application to Exploration and Production (E&P) vessels includes:
A. Inspection Coverage
All pressure vessels used in E&P services such as drilling, producing, gathering, transporting, lease processing, and treating liquid petroleum, natural gas, and associated saltwater (brine) can be inspected.
B. Applicability of Sections
Except for Section 6, all sections of the inspection code are applicable to pressure vessels in E&P service.
C. Alternative Rules in Section 9
The alternative rules in Section 9 are designed for services that may be regulated under various authorities such as:
- U.S. Coast Guard
- Office of Hazardous Materials Transportation (DOT)
- Minerals Management Service (Department of the Interior)
- State and local oil and gas agencies
- Other regulatory commissions
2. Excluded and Optional Services
The scope of API 510 includes specific application areas where certain services are excluded or optional. Here’s a structured breakdown:
A. Excluded Services
- Pressure vessels on movable structures covered by other jurisdictional regulations (refer to Appendix A (a)).
- All classes of containers listed for exemption in the scope of the applicable construction code (refer to Appendix A (b)). Pressure vessels that do not exceed the volumes and pressures listed in Appendix A (c).
B. Optional Services
Services beyond the specific requirements outlined in the inspection code may be considered on a case-by-case basis, depending on regulatory requirements and industry standards.
3. Recognized Technical Concepts
This inspection code acknowledges the use of fitness-for-service concepts to assess damage in pressure-containing components during operation. API 579 offers detailed procedures for evaluating specific types of damage mentioned in this code.
Additionally, the inspection code incorporates risk-based inspection (RBI) concepts to determine when inspections should occur. API 580 provides guidelines for conducting these risk-based assessments.
In conclusion, the scope of API 510, as outlined in the 2006 version, includes specific criteria for pressure vessel inspection, excluding certain categories such as pressure vessels on movable structures covered by other regulations, exempt containers, and vessels within defined volume and pressure ranges. It also acknowledges fitness-for-service and risk-based inspection concepts, with detailed assessment procedures provided by API 579 and API 580, respectively.
Unlock API 510 Compliance Success with PetroSync’s Expert Training
Please be aware that this information references the 2006 edition of API 510 and may need updates to reflect the most recent standards. However, grasping the core elements of API 510 training remains essential to determining if it covers the equipment you manage.
Given the importance of safety and efficiency in industrial settings, obtaining API 510 certification through PetroSync can deliver significant benefits. This certification establishes a thorough framework for inspecting, repairing, and maintaining pressure vessels, ensuring that they fulfill safety standards and function efficiently.
Earning the API 510 certification showcases your dedication to safety protocols and enhances your professional standing, adding value to your role in the industry. PetroSync’s API 510 training offers the expertise needed to evaluate pressure vessel integrity, detect potential problems early, and implement preventive strategies, all of which contribute to a safer and more reliable workplace.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.






