- Storage tank repair is a strategic asset integrity move that protects safety, compliance, and long-term operational performance across high-risk industries.
- Proactive repair prevents corrosion-driven failures, cutting safety incidents, environmental exposure, and costly legal or reputational fallout.
- Planned maintenance and predictive scheduling extend tank life by decades while reducing downtime and avoiding expensive asset replacement.
- Quality repairs rely on certified welding, corrosion protection, and rigorous post-repair inspection to restore strength and reliability.
- Skilled teams and continuous training turn maintenance from reactive fixes into a data-driven strategy that supports sustainable business performance.
Storage tank repair plays a critical role in ensuring safe, reliable, and efficient industrial operations across the oil and gas, petrochemical, manufacturing, and power generation sectors. Storage tank function as essential assets within the production chain—responsible for holding crude oil, refined products, chemicals, water, and various industrial fluids that support continuous operations and regulatory compliance.
When these tanks deteriorate due to corrosion, structural damage, or mechanical failure, the consequences extend far beyond equipment issues. The impact may lead to production interruptions, safety hazards, rising operational costs, environmental exposure, and even reputational and legal consequences for an organization.
For senior leaders, maintenance managers, and executives responsible for asset integrity, storage tank repair is no longer only a technical requirement—it is a strategic priority.
The conversation has shifted from “How do we repair damage when it appears?” to “How do we prevent failures, minimize downtime, and secure long-term operational performance?” A proactive and well-executed repair strategy strengthens reliability, maximizes safety, improves cost efficiency, and protects business sustainability in increasingly competitive industrial environments.
What is Storage Tank Repair?
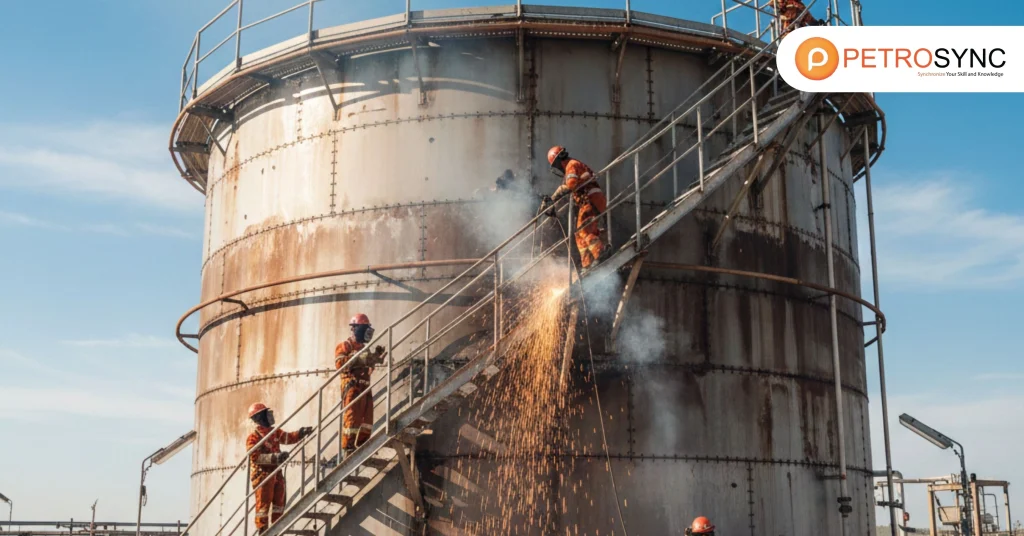

Storage tank repair involves engineering actions aimed at restoring the mechanical strength, containment reliability and operational performance of industrial tanks used to store hydrocarbons, chemicals and process fluids. Typical repair work includes replacing corroded shell plates or bottoms, repairing roofs, reinforcing structural elements, addressing weld failures or installing new internal coatings and linings.
These activities must comply with industry standards such as API 650, API 653 and API 579, ensuring the tank remains fit for service while maintaining safety and reliability. Effective tank repair is a continuous improvement strategy—identifying degradation early, applying the right repair techniques and validating the results through inspection and quality assurance testing.
In short, tank repair bridges the gap between deterioration and readiness—rebuilding confidence in the asset’s ability to perform safely and efficiently.
Why is Storage Tank Repair Important in Industrial Operations?
1. Preventing Safety and Environmental Hazards
Storage tanks often contain hazardous and flammable materials. Structural failure—such as leaks, ruptures or collapse—can lead to fires, explosions or major environmental contamination. Research published in industry-safety literature examined over 200 tank incidents and showed that most failures were related to corrosion and material fatigue, and many of them could have been prevented with timely inspection and repair.
Performing repairs before damage escalates protects both workforce and the surrounding environment, reinforces regulatory compliance and prevents costly emergency response actions and legal consequences.
2. Extending Tank Life and Reducing Costs
At first glance, postponing repair may appear cost-saving. However, delayed maintenance accelerates degradation, requiring far more expensive structural replacements later. Engineering analysis demonstrated that structured integrity assessment combined with planned repair can extend storage tank service life by up to 20 additional years, significantly reducing capital expenditure.
Proactive repair transforms maintenance from a reactive cost center into a lifecycle-value strategy—reducing downtime, minimizing asset replacement frequency and improving overall financial performance.
3. Maintaining Operational Reliability and Compliance
Unexpected tank shutdowns disrupt refinery throughput, supply chain scheduling and product distribution. A maintenance optimisation study revealed that predictive repair scheduling achieved more than 90% accuracy in prioritising tank maintenance activities, helping companies prevent unplanned shutdown events.
For leaders responsible for profitability, consistent availability and regulatory compliance, storage tank repair ensures reliability, operational continuity and smooth progression through audits and inspection cycles.
Common Types and Methods of Storage Tank Repair
1. Structural Repair and Welding Techniques
Structural repairs restore or reinforce critical tank components such as shell plates, bottom plates, roof structures, stiffeners and anchoring systems. Welding methods—including lap-plate welding, butt-joint replacement and reinforcement installations—are chosen based on defect type and stress requirements.
Engineering studies highlight that reinforced plate welding significantly improves tank stability, especially under mechanical and thermal load. Because structural repair directly influences tank strength, welding must follow strict qualification processes and be validated using post-repair inspection methods.
2. Coating, Lining and Corrosion Protection
Corrosion remains one of the most common causes of tank deterioration. After structural repair is completed, applying advanced protective coatings or linings and integrating corrosion control solutions such as cathodic protection or inhibitors is essential for controlling long-term damage.
A technical review in materials engineering emphasised that modern coatings paired with advanced inspection technologies significantly improve corrosion resistance and extend maintenance intervals. Improving corrosion control reduces risk, safeguards product quality and prevents repetitive repair cycles.
3. Inspection and Testing after Repair
The reliability of any repair depends on thorough validation. Post-repair verification includes non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic thickness testing, magnetic particle inspection, dye penetrant testing, radiographic inspection, and hydrostatic or pneumatic pressure tests.
Quality assurance research confirms that structured inspection procedures and documentation frameworks dramatically decrease failure recurrence and improve remaining-life estimation accuracy—providing measurable assurance to operational leaders.
Ensuring System Integrity through Best Practices
1. Scheduled Maintenance and Condition Monitoring
Storage tank integrity should rely on maintenance planning that integrates scheduled inspections, real-time condition monitoring and predictive maintenance models. Analytical studies across tank facilities identified structural condition and maintenance overdue status as the most influential parameters in determining repair priority.
With data-driven planning, companies shift away from reactive emergency repairs toward strategic asset health management—reducing downtime and stabilising budgets.
2. Adhering to Industry Standards
Standards such as API 650, API 653 and API 579 / ASME FFS-1 outline requirements for inspection intervals, repair decision-making and safe return-to-service criteria. Adherence ensures technical quality, legal compliance and optimal asset performance.
For executives, regulatory compliance is not only mandatory—it is essential for operational credibility and risk reduction.
3. Skilled Workforce and Safety Management
Repair work requires high competency due to hazards associated with confined spaces, welding, heavy equipment, pressurised systems and chemical exposure. Engineering research consistently shows that well-trained teams reduce rework, improve repair accuracy and enhance incident-free performance.
Investment in skill development is an investment in reliability, safety culture and operational excellence.
Strengthening Asset Integrity with Continuous Learning
1. The Role of Technical Expertise in Effective Repairs
Selecting the right repair technique requires understanding degradation mechanisms such as metal loss, cracking, settlement or deformation. Research in advanced inspection methodology shows that emerging technologies—robotic inspection tools, drones, digital twin modelling and automated NDT—enable faster and more precise assessment, supporting more effective repair decisions.
Expert capability drives better outcomes and maximises return on repair investment.
2. Why Ongoing Training Improves Maintenance Reliability
Studies on predictive maintenance effectiveness demonstrate measurable reductions in operational interruptions when maintenance personnel receive structured technical training and decision-support tools.
Training aligns asset integrity goals with organisational performance outcomes and ensures sustainability of repairs—not short-term fixes.
Advance Your Storage Tank Repair Skills with PetroSync Training
For leaders seeking to strengthen tank integrity management, improve operational continuity and reduce risk, developing internal expertise is a critical competitive advantage. Technology alone is not enough—capability must follow strategy.
PetroSync provides specialised training programmes designed for engineers, inspectors, asset integrity professionals and senior decision-makers. The programme covers:
- Root-cause degradation analysis and damage mechanism identification
- Advanced repair methods aligned with industry standards (API, ASME)
- Real-world case studies for structural repair and corrosion control
- Condition monitoring and predictive maintenance frameworks
- Risk-based inspection principles and remaining life calculations
- Best-practice safety and execution management
Participants gain the knowledge needed to make confident repair decisions, minimise downtime, reduce maintenance cost and sustain asset reliability.
If your organisation aims to move from reactive maintenance to strategic performance improvement, PetroSync training can accelerate your progress and deliver measurable results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Storage tank repair involves restoring the mechanical strength, containment reliability, and operational performance of industrial tanks through activities such as replacing corroded plates, repairing roofs, reinforcing structures, and applying new coatings. It is necessary to ensure safety, prevent leaks or failures, maintain compliance with industry standards, and keep tanks fit for continued service.
Delaying storage tank repair can lead to serious safety hazards, environmental contamination, unplanned shutdowns, higher maintenance costs, regulatory violations, and potential legal and reputational consequences. Corrosion and structural degradation may escalate into leaks, fires, or catastrophic failures if not addressed in time.
Planned and proactive storage tank repair slows degradation, prevents major structural damage, and can extend tank service life by many years. This approach reduces the need for full tank replacement, minimizes downtime, lowers long-term maintenance costs, and improves overall lifecycle asset value.
Common storage tank repair methods include structural welding and plate replacement, roof and bottom repairs, application of protective coatings and linings, corrosion control systems such as cathodic protection, and post-repair inspection using non-destructive testing and pressure testing to verify integrity.
Industry standards such as API 650, API 653, and API 579 provide clear requirements for inspection, repair decisions, and fitness-for-service evaluation. Following these standards ensures repairs are technically sound, legally compliant, and aligned with best practices for safety, reliability, and long-term operational performance.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.