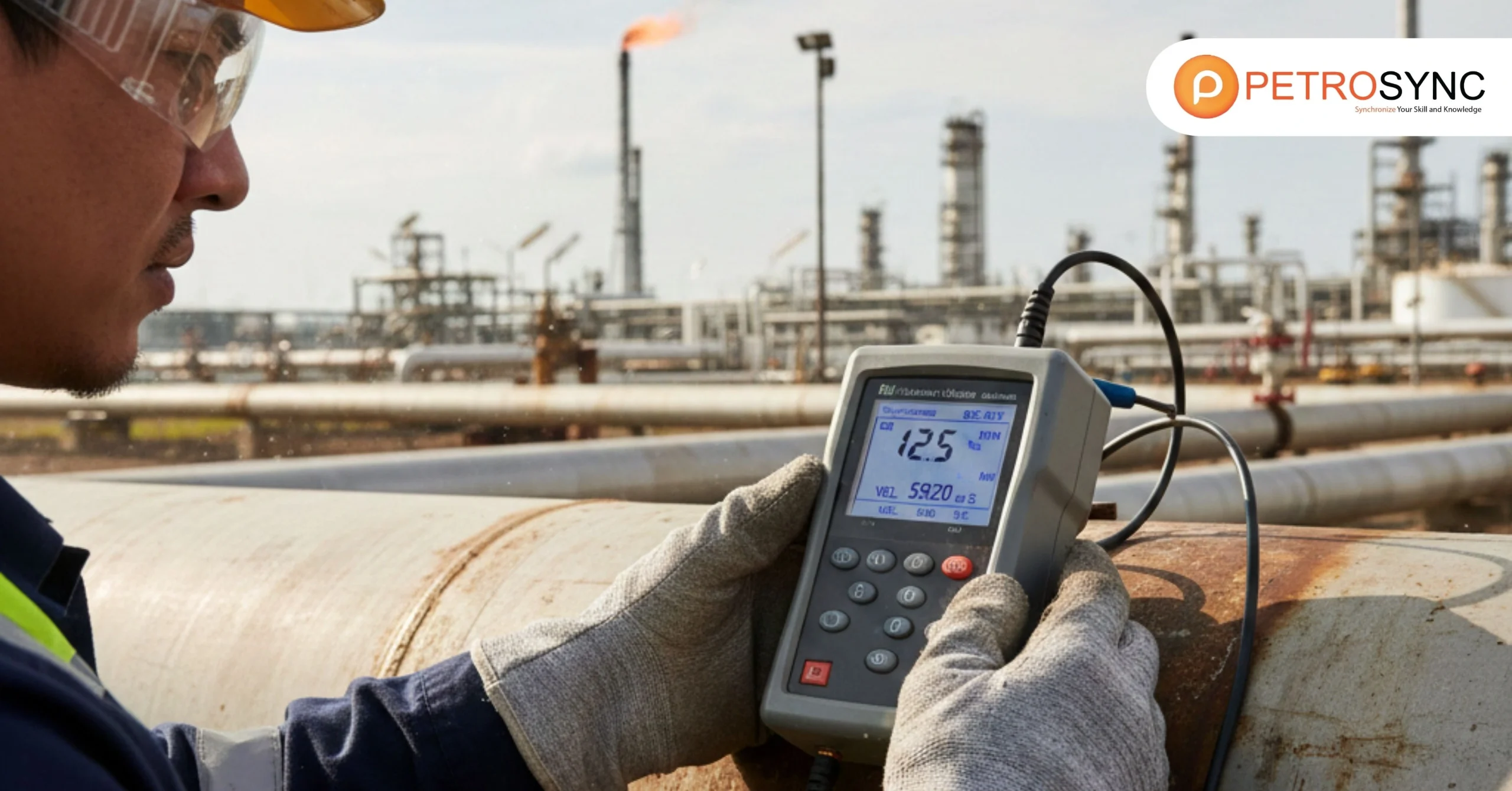
Wall Thickness Measurement is a critical practice in oil and gas operations, ensuring reliability, safety, and long-term asset performance. Every system, pipeline, and pressure-containing equipment faces significant mechanical, chemical, and thermal stress, gradually degrading over time. Corrosion and erosion are inevitable and often go unnoticed until a failure occurs.
That is why wall thickness measurement is not just a maintenance task—it is a strategic responsibility that safeguards personnel, assets, and operational continuity. Many leaders across upstream, midstream, and downstream operations recognize the importance of inspection. However, the difference between organizations that thrive and those that struggle lies in how accurate, consistent, and data-driven their measurement strategies are.
Research in pipeline integrity and corrosion behavior shows that even small reductions in wall thickness can sharply increase the probability of rupture or leakage, causing costly shutdowns and safety or environmental incidents. Studies indicate that once a component loses roughly 40% of its original wall thickness, the likelihood of failure rises significantly, often escalating rapidly as thinning continues.
When measured consistently and precisely, wall thickness measurement does more than quantify metal loss—it empowers decision-makers to predict remaining life, optimize maintenance budgets, and drive operational excellence. Before exploring specific methods, let’s understand what wall thickness measurement truly entails and why it is indispensable in industrial practice.
What Is Wall Thickness Measurement?

Engineers widely employ wall thickness measurement to assess the thickness, integrity, and physical properties of materials using high-frequency sound waves.. It plays a crucial role in product testing and quality control, ensuring compliance with desired standards.
How Do You Measure Wall Thickness?
You can utilize two techniques—the tangential technique and the double wall technique—to conduct wall thickness measurements, including both external and internal pitting assessments. These methods enable accurate determination of material thickness and identification of any pitting-related issues.
1. Tangential Radiographic Technique
The Tangential technique measures wall thickness by placing the probe or sensor in direct contact with the material’s surface. By positioning the probe at a specific angle, this technique enables accurate measurement of the material’s thickness and the detection of any irregularities or anomalies.
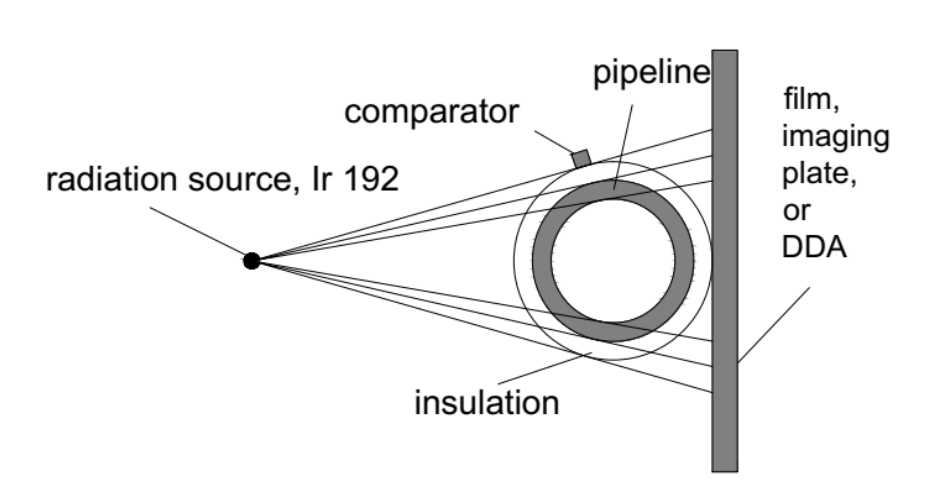 Figure 1. Tangential Radiographic Inspection Set-Up. Adapted from “Utilization and Validation of Tangential Radiographic Technique in Wall Thickness Measurement,” by M. F. H. Chowdhury, and M. A. Habib, 2019. Copyright 2019 by Nuclear Science and Applications.
Figure 1. Tangential Radiographic Inspection Set-Up. Adapted from “Utilization and Validation of Tangential Radiographic Technique in Wall Thickness Measurement,” by M. F. H. Chowdhury, and M. A. Habib, 2019. Copyright 2019 by Nuclear Science and Applications.
The TRT method provides an indirect approach for measuring wall thickness. To ensure accurate measurements, calibration is necessary. In this technique, technicians affix a reference block with known dimensions to the test object’s surface during exposure. They then calibrate the resulting radiographic image based on the reference block’s dimensions.
By referencing this calibrated image, the wall thickness of the pipe can be accurately determined. This approach enhances measurement precision and enables effective evaluation of wall thickness using radiographic imaging.
2. Double Wall Technique
The Double Wall Technique is a method used for measuring wall thickness. It involves inserting the probe or sensor between two parallel walls to measure the thickness between them. This technique is particularly useful when direct access to both sides of the material is not possible.
Using the Double Wall Technique allows professionals to obtain accurate wall thickness measurements, providing valuable insights into the material’s structural integrity. Various industries—such as manufacturing, construction, and maintenance—widely apply this technique to ensure the quality and safety of structural components.
3. Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a widely used technique for measuring wall thickness. It works by sending high-frequency sound waves into the material being examined. These sound waves travel through the material and bounce back when they encounter the opposite wall.
By measuring the time it takes for the sound waves to return, we can accurately determine the thickness of the wall. UT is applicable to different materials like metals, plastics, and composites, making it a versatile and valuable method for measuring wall thickness in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and maintenance.
4. Calipers
Technicians commonly use calipers to measure wall thickness. The tool has two adjustable arms with pointed ends that fit around the material. After they close the arms around the material and read the scale, they obtain an accurate wall thickness measurement.
Industries such as manufacturing, construction, and quality control widely utilize calipers to measure thin materials and ensure compliance with specifications and standards.
5. Eddy Current Testing (ECT)
Eddy Current Testing (ECT) is a non-destructive method used for measuring wall thickness. It relies on electromagnetic induction to assess the thickness of conductive materials. During ECT, a probe is moved across the material’s surface, generating magnetic fields. These fields create electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the material.
Any variations in thickness affect the eddy currents, allowing the detection and measurement of wall thickness irregularities. ECT is commonly used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing for quick and reliable thickness measurements in quality control and inspection processes.
6. Magnetic Induction
Magnetic Induction is a method used for measuring wall thickness. It operates based on the principles of electromagnetic induction to assess material thickness. In this technique, a magnetic field is generated and applied to the material under inspection.
Variations in thickness cause alterations in the magnetic field, which can be detected and correlated with the wall thickness. Magnetic Induction is particularly effective for measuring the thickness of materials that are not magnetic. This approach finds wide application in different industries to ensure the reliability and integrity of structural components.
7. Laser Measurement
Laser Measurement is a technique employed for measuring wall thickness. It utilizes laser technology to accurately determine the distance between the laser source and the material’s surface. By measuring this distance, an indirect measurement of the wall thickness can be obtained.
Laser Measurement is known for its precise and non-contact nature, making it suitable for a wide range of materials and applications. It finds common use in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and quality control, where accurate wall thickness measurements are crucial for ensuring product integrity and adherence to specifications.
What Is The Purpose of Wall Thickness Measurement?
The purpose of conducting wall thickness measurement testing is to:
- Ensure adherence to design specifications, industry standards, and safety regulations.
- Detect potential issues such as corrosion, erosion, thinning, or structural weaknesses.
- Facilitate timely maintenance, repair, or replacement of components.
- Safeguard the integrity, safety, and performance of the structure or material.
- Provide accurate data for informed decision-making regarding maintenance, repair, or replacement actions.
- Monitor and prevent degradation or failure of structural components.
- Verify the quality and reliability of manufacturing processes.
- Support quality control and assurance initiatives across various industries.
- Enhance the longevity and dependability of structures and materials.
- Optimize the efficient utilization of resources.
In conclusion, wall thickness measurement is a crucial factor that ensures the safety and durability of industrial piping systems. As discussed in this article, precise wall thickness assessments are particularly important in industries like oil and gas, power, and petrochemicals, where the strength of structures is of utmost importance.
By using accurate measurement techniques, piping inspectors can identify potential weaknesses, corrosion, and erosion, enabling them to make well-informed decisions regarding maintenance, repairs, or replacements.
As these industries continue to grow, wall thickness measurement plays a crucial role in maintaining efficiency and reducing risks. Especially for piping inspectors, wall thickness measurement remains a crucial tool to help them decide further action for the overall equipment’s reliability and safety.
API 570 regulates wall thickness measurement in industrial piping inspections, ensuring safety and operational requirements are met. Inspectors follow the code to assess corrosion and erosion levels, considering the material, operating conditions, and system lifespan for informed decision-making.
Join Our PetroSync Training and Build Competitive Advantage
PetroSync’s API 570 training equips you as piping inspectors with expertise in adhering to regulations and utilizing accurate measurement techniques. The course covers best practices, advanced technology, and result interpretation for reliable and efficient industrial operations.
Investing in API 570 training with PetroSync enhances inspector skills, ensuring piping system integrity and risk mitigation. Staying updated with standards safeguards assets and personnel, contributing to overall industry reliability and safety. Reserve your API 570 training course spot and enhance your inspection, repair, alteration, and rerating piping systems with PetroSync!

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.