Flanged Joint plays a critical role in ensuring safe and reliable piping connections across the oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation industries. In systems where extreme pressure, temperature fluctuations, and corrosive chemicals are common, the integrity of every connection point becomes essential for maintaining operational continuity and asset reliability.
A single failure within a piping network—particularly at its joints—can trigger severe consequences, including costly unplanned shutdowns, safety risks, and significant environmental impact. The high operational stakes highlight why selecting the right connection method is more than a technical choice—it is a strategic decision for long-term facility performance.
For many facilities and engineering teams, flanged joints remain the preferred solution due to their balance of strength, adaptability, and maintenance accessibility. Beyond joining pipe sections, flanged joints support efficient inspection, repair, and replacement activities, making them crucial for achieving enhanced reliability and minimizing downtime.
Plant managers, engineers, and decision-makers gain insight to improve system safety and optimize operational performance by understanding how flanged joints work, where they are used, and their material options and key advantages.
What Is A Flanged Joint?
Credit: instrumentationtools.com
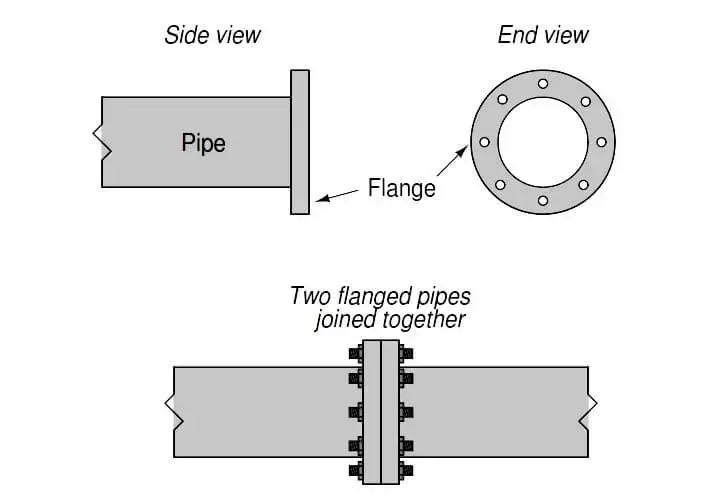
A flanged joint is a way to connect pipes, where the connecting pieces have flanges used to bolt the parts together. Although the word ‘flange’ generally refers to the actual raised rim or lip of fitting, many plumbing fittings with flanges are also called flanges themselves.
The flanges are carefully positioned and firmly fastened with bolts and nuts, creating a secure and leak-resistant connection. Flanged joints offer numerous benefits, notably easy assembly and disassembly, which prove convenient for maintenance, repairs, or alterations.
Flanged joints find extensive application across diverse industries, encompassing petrochemical, oil and gas, chemical, and power sectors. The selection of the appropriate flanged joint type is influenced by factors like pressure, temperature, and the size of the piping system.
Where Are Flanged Joints Used For?
Flanged pipes are commonly used for aboveground applications when a sturdy, secure connection is required for liquids like water, wastewater, air, and oil. They are extensively utilized in water treatment plants, wastewater treatment plants, industrial piping systems, and both indoor and outdoor applications such as bridges and elevated crossings.
Using flanged joints underground is generally not advisable due to the inflexible nature of the joint. This recommendation is supported by the appendices found in relevant ANSI/AWWA standards.
What Material Is Used For Flanged Joint?
Flanged joints can be made from various materials depending on the specific application and requirements.
- Carbon steel
- Alloy
- Stainless
The choice of material depends on factors like the conveyed fluid, temperature, pressure, corrosion resistance, and environmental conditions.
What Are The Most Commonly Used Flanged Types in The Petrochemical Industry?
In the petrochemical industry, several flanged types are commonly used for connecting pipes, valves, and equipment. Some of the most frequently utilized flanged types include:
1. Welding Neck Flange
A welding neck flange is a type of flange designed for welding to a pipe. It provides a smooth connection and adds strength. It is used in high-pressure applications and requires skilled welding for a reliable joint.
2. Slip On Flange
A slip-on flange slides over a pipe and welders then secure it in place. It serves low-pressure applications, installs easily, and provides a secure connection when welded properly.
3. Socket Weld Flange
A socket weld flange connects to a pipe using socket welding. It fits over the pipe end and welders join it around the flange’s outer perimeter. Engineers use it in small pipe sizes and low-pressure applications, ensuring a strong and leak-free connection when welded properly.
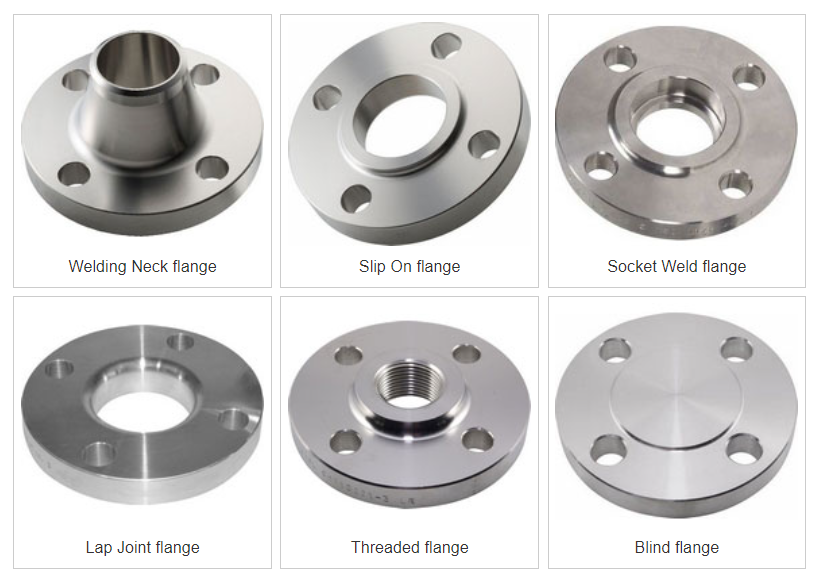

4. Lap Joint Flange
A lap joint flange consists of two parts: a flat disc with a raised inner ring and a collar. TThe pipe receives the slipped-on collar, and the flange rests on it. Workers secure the connection with bolts. Lap joint flanges facilitate easy disassembly and suit situations requiring pipe adjustments or changes They are cost-effective but not suitable for high-pressure situations.
5. Threaded Flange
A threaded flange screws onto the pipe end for an easy and secure connection. People commonly use it in low-pressure applications but do not recommend it for high-pressure situations.
6. Blind Flange
A blind flange is a type of flange used to seal the end of a pipe or vessel. It blocks the flow of fluid or gas and provides a secure seal. It is commonly used for temporary or permanent closure during maintenance or inspections. Blind flanges are easy to install and can be removed when needed.
What Are The Advantages of Flanged Joints?
Flanged joints provide several advantages in various applications:
1. Strong and Secure Connection
Flanged joints offer a sturdy and dependable connection between pipes or components. The use of bolts and flanges ensures a robust joint that can withstand high pressure and stress.
2. Leak Resistance
The raised rims or lips of flanges create a tight seal when bolted together, minimizing the risk of leaks. This is especially important when dealing with fluids or gases under pressure, ensuring efficient and safe fluid transportation.
3. Easy Installation and Maintenance
Flanged joints allow for straightforward installation and disassembly, making maintenance, repairs, and component replacement easier. This convenience reduces downtime and improves overall operational efficiency.
4. Alignment Flexibility
Flanged joints provide flexibility in aligning pipes or equipment during installation. They can be adjusted or rotated to ensure precise alignment, even when dealing with misaligned or non-uniform components.
5. Compatibility and Standardization
Flanged joints adhere to standardized dimensions and designs, ensuring compatibility between pipes and components from different manufacturers. This interchangeability simplifies system integration and the replacement of parts.
6. Thermal Expansion Accommodation
Flanged joints can accommodate thermal expansion and contraction in piping systems. They allow for slight movements without compromising the integrity of the joint, reducing the risk of stress-related failures.
7. Versatility
Flanged joints are suitable for a wide range of applications and industries, including plumbing, oil and gas, and chemical processing. They can handle various fluids, pressures, and temperatures, making them highly versatile.
8. Longevity and Durability
Properly installed and maintained flanged joints offer long-lasting durability. Engineers design them to withstand challenging environmental conditions, corrosion, and wear, ensuring reliable and extended service life.
It’s important to note that the specific benefits and suitability of flanged joints may vary depending on the application, system requirements, and adherence to industry standards. Following recommended procedures for installation and maintenance is crucial to maximize the advantages of flanged joints.
What Are The Disadvantages of Flanged Joints
While flanged joints offer various advantages, it’s important to be aware of their drawbacks:
1. Cost
Flanged joints can be more expensive than other types of connections due to the additional components required, such as flanges, bolts, and gaskets.
2. Stress Concentration
Flanged joints can create stress concentration points due to the bolt holes and the transition between the flange and the pipe, potentially increasing the risk of fatigue or corrosion cracking.
3. Limited Adaptability
Flanged joints are not as adaptable to changes or modifications compared to other types of connections. Altering or reconfiguring the system may require the removal and replacement of entire flanged sections.
4. Complex Installation
Proper installation of flanged joints requires skilled labor and knowledge of tightening procedures to ensure a leak-free connection, making the installation process more complex.
Proper design, installation, and maintenance practices can mitigate the drawbacks of flanged joints, but engineers must carefully assess their suitability for each application.
Piping inspectors, particularly those holding API 570 certification, play a crucial role in minimizing the disadvantages associated with flanged joints. Their expertise ensures correct installation, adherence to standards, and early identification of issues like incorrect tightening, alignment problems, or inadequate gasket selection. This proactive approach optimizes flanged joint performance, enhancing reliability and reducing drawbacks.
Join PetroSync Training for Real Industry Expertise
Petrosync, a leading provider of industry knowledge and training, offers comprehensive and in-depth materials on API 570. Our training delves into the intricacies of API 570, focusing on the inspection, repair, alteration, and rerating of in-service piping systems.
With a thorough understanding of API 570 standards, PetroSync is on a mission to provide you with the necessary expertise to effectively assess the integrity of piping systems and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Through our detailed materials, our API 570 training empowers you with the knowledge and skills required to perform critical tasks related to piping inspection and maintenance, contributing to the safe and reliable operation of industrial facilities.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.