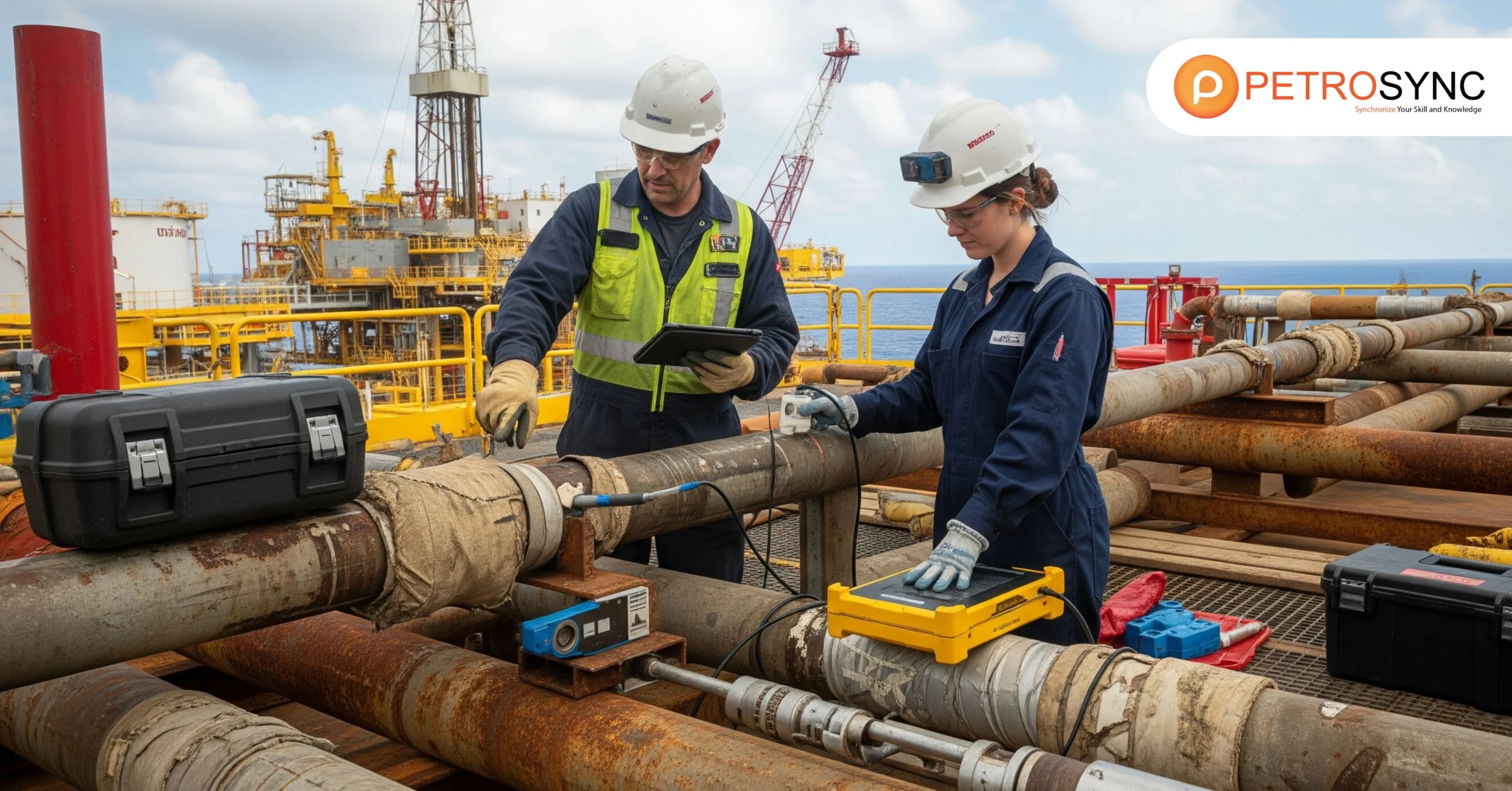
Reliability Engineering Industries are driving progress across asset-intensive sectors by ensuring operational excellence, minimizing downtime, and maximizing the lifespan of critical equipment. In today’s competitive industrial environment, businesses face increasing pressure to maintain consistent performance while optimizing costs.
Reliability engineering has emerged as a strategic discipline that focuses on the systematic design, operation, and maintenance of systems to ensure they function reliably over time.
By embedding reliability engineering principles, industries can achieve measurable improvements in efficiency, reduce operational risks, and strengthen overall business resilience.
Beyond its technical role, reliability engineering acts as a strategic enabler—helping companies anticipate failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. This approach is especially crucial in high-stakes sectors such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and energy, where equipment failures can lead to substantial financial losses, safety hazards, and environmental impacts.
What are Reliability Engineering Industries?
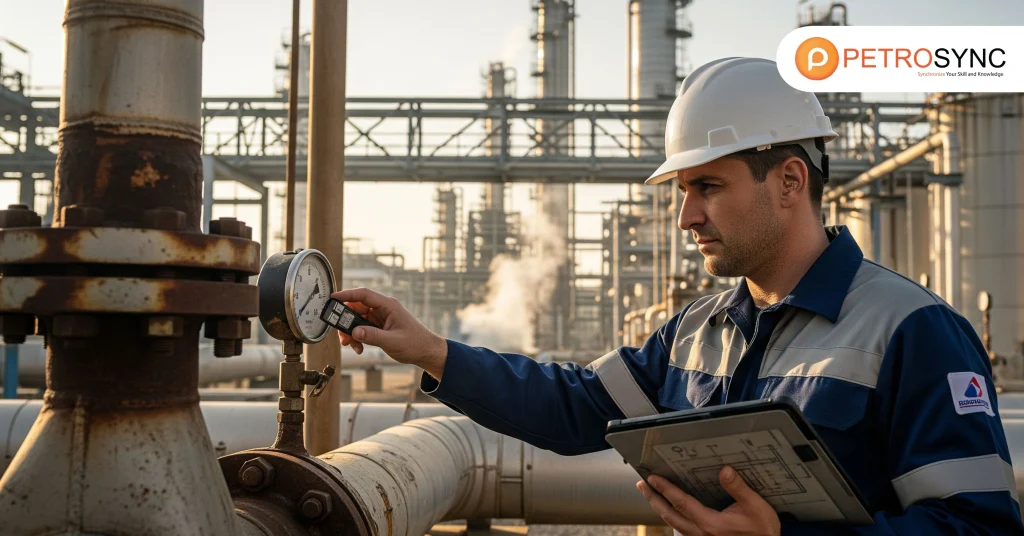

Reliability engineering industries include sectors where operational continuity is essential. This encompasses oil and gas, energy, manufacturing, transportation, and even high-tech production. These industries rely on assets that must perform consistently and safely. Reliability engineering applies engineering principles, predictive analytics, and structured maintenance practices to ensure these assets function as intended.
The core goal is to reduce unexpected failures, improve system uptime, and support business continuity. In oil and gas, for example, pipeline or drilling equipment failure can halt operations, cost millions, and compromise safety. Implementing structured reliability engineering prevents such scenarios and strengthens operational resilience.
Why Reliability Engineering Industries are Crucial for Business
Investing in reliability engineering translates into tangible business advantages:
- Operational Continuity: By predicting and preventing failures, companies maintain consistent operations, ensuring that production targets and customer commitments are met.
- Cost Reduction: Proactive maintenance and system optimization reduce unplanned downtime and extend the life of costly equipment, directly impacting the bottom line.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to reliability standards ensures compliance with safety and industry regulations, avoiding fines and reputational damage.
- Market Competitiveness: Businesses that deliver reliable performance differentiate themselves, building trust with clients and stakeholders.
Studies in industrial sectors indicate that effective reliability programs can reduce equipment downtime by up to 30% while boosting operational efficiency by 20%, underscoring its strategic importance.
Benefits of Reliability Engineering Industries
1. Improving Operational Efficiency
Reliability engineering identifies bottlenecks and inefficiencies in processes, enabling organizations to optimize workflows and maintain peak performance. Techniques such as predictive maintenance use real-time data to forecast potential failures, allowing interventions before production is impacted. This proactive approach improves throughput, reduces waste, and increases overall efficiency.
2. Reducing Equipment Downtime
Unplanned downtime is one of the most significant cost drivers in asset-intensive industries. Reliability engineers utilize methods like root cause analysis and failure mode effects analysis (FMEA) to detect underlying issues, implement corrective actions, and prevent recurrence.
Companies with robust reliability programs report a noticeable reduction in downtime, sometimes cutting losses by hundreds of thousands of dollars annually in large-scale operations.
3. Supporting Predictive and Preventive Maintenance Programs
Reliability engineering supports both predictive and preventive maintenance. Predictive maintenance relies on monitoring equipment conditions and analytics to anticipate failures. Preventive maintenance schedules routine inspections and servicing based on asset history and criticality.
Together, these approaches enhance equipment reliability, reduce maintenance costs, and improve safety.
Key Components of Reliability Engineering Industries
1. Asset Reliability and Performance Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of asset health is the backbone of reliability engineering. By collecting operational data and analyzing trends, organizations can detect anomalies early, predict failures, and make data-driven maintenance decisions.
2. Maintenance Strategies and Best Practices
Implementing maintenance strategies such as Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) and condition-based maintenance ensures that resources are allocated effectively, prioritizing the most critical assets. Best practices in maintenance planning also reduce operational disruptions and maximize asset lifespan.
3. Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Reliability engineers assess risks systematically, identifying potential points of failure and their consequences. This enables organizations to implement mitigation strategies, improve safety, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
4. Continuous Improvement and Data Analysis
Continuous improvement is integral to reliability engineering. Organizations leverage data analytics to monitor performance metrics, identify improvement areas, and refine maintenance strategies. This iterative process fosters innovation and ensures long-term operational excellence.
Challenges and Opportunities in Reliability Engineering Industries
1. Common Operational and Technical Challenges
Challenges include complex system interactions, limited visibility into real-time data, and resistance to change within organizations. Overcoming these requires strategic planning, investment in technology, and a culture that embraces continuous improvement.
2. Knowledge and Skills Gaps in Teams
Reliability engineering requires specialized skills. Knowledge gaps can impede performance, especially as technology evolves. Structured training programs and continuous professional development are essential to equip teams with the capabilities needed for modern reliability challenges.
3. Integrating Technology and Data Analytics Effectively
Advanced technologies, including IoT sensors, AI, and machine learning, offer immense potential for predictive and prescriptive maintenance. Proper integration of these technologies requires data governance, alignment with business goals, and ongoing skills development.
Advance Your Reliability Engineering Expertise with PetroSync Training
Investing in reliability engineering knowledge is crucial for professionals aiming to excel in asset-intensive industries. PetroSync Training offers comprehensive programs designed for managers, senior engineers, and executives seeking to elevate their expertise. The training covers best practices, emerging technologies, and advanced reliability methodologies.
By joining PetroSync, participants gain the skills to implement effective maintenance strategies, optimize operational efficiency, and reduce downtime. Beyond personal growth, these programs empower organizations to achieve operational excellence, strengthen competitiveness, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Professionals who complete PetroSync training report enhanced confidence in decision-making and measurable improvements in asset performance, making it an indispensable investment for forward-looking companies.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.